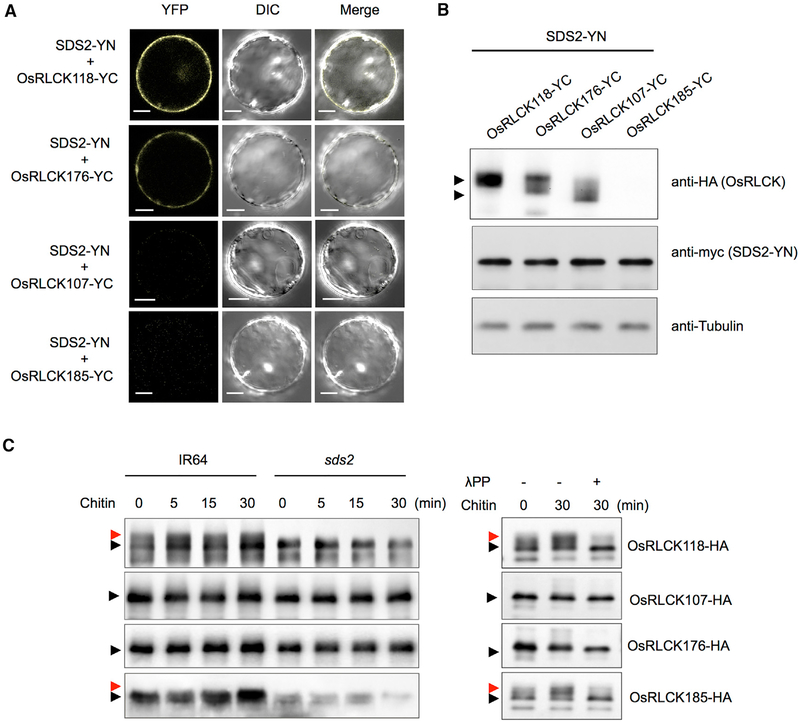
Figure 5. SDS2 Interacts with and Phosphorylates OsRLCK118.
(A) BiFC analysis of the SDS2-OsRLCK118 or OsRLCK176 interactions in rice protoplasts. SDS2 and OsRLCKs were fused to the N and C termini of YFP, respectively. Protoplasts were observed with a confocal microscope 48 hr after transfection. YFP, DIC, and merged channels were labeled on the top of the pictures. Scale bars represent 10 μm.
(B) Detection of protein levels in BiFC assays in (A). Anti-HA and anti-myc were used to detect OsRLCKs-YC and SDS2-YN, respectively. Anti-tubulin was used to determine protein loading amount. Arrows indicate OsRLCK118, OsRLCK176, and OsRLCK107. OsRLCK185 was too low to detect.
(C) Detection of OsRLCKs in vivo phosphorylation by SDS2. Plasmids of OsRLCKs with HA tag are transfected into wild-type (IR64) and sds2 mutant protoplasts, separately. Transfected protoplasts are treated with 5 μg/mL chitin for 0, 5, 15, and 30 min. Phosphorylation of OsRLCK is determined by band shift. Black and red arrows indicate unphosphorylated and phosphorylated band, respectively (left panel). The phosphorylation is confirmed by treatment of lambda protein phosphatase (λPP) (right panel). − and + indicate with or without λPP treatment. See also Figure S5.