Figure 3.
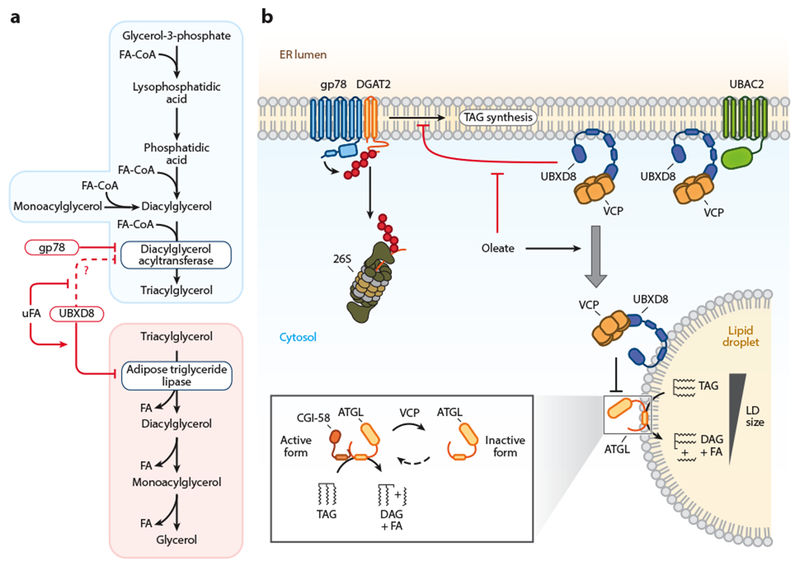
ERAD regulation of triacylglycerol metabolism. (a) Schematic of the triacylglycerol synthesis and degradation pathways with the points of ERAD-mediated regulation indicated. Regulated enzymes are shown in blue boxes and ERAD machinery in red boxes. (b) Constitutive DGAT2 degradation is mediated by gp78. Under low FA conditions, UBXD8 inhibits TAG synthesis. Increases in FA levels release UBXD8 inhibition of TAG synthesis and promote UBXD8 trafficking to LDs. On LDs, UBXD8 impairs lipolysis through the dissociation of ATGL from its cofactor CGI-58. Abbreviations: ATGL, adipose triglyceride lipase; DAG, diacylglycerol; DGAT, diacylglycerol acyltransferase; ERAD, endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation; FA, fatty acid; uFA, unsaturated fatty acid; FA-CoA, fatty acid coenzyme A; gp78, glycoprotein 78; LD, lipid droplet; TAG, triacylglycerol; UBAC2, UBA domain–containing protein 2; UBXD8, UBX domain–containing protein 8; VCP, valosin-containing protein.
