Figure 2. Mechanisms of amyloid beta clearance from the brain.
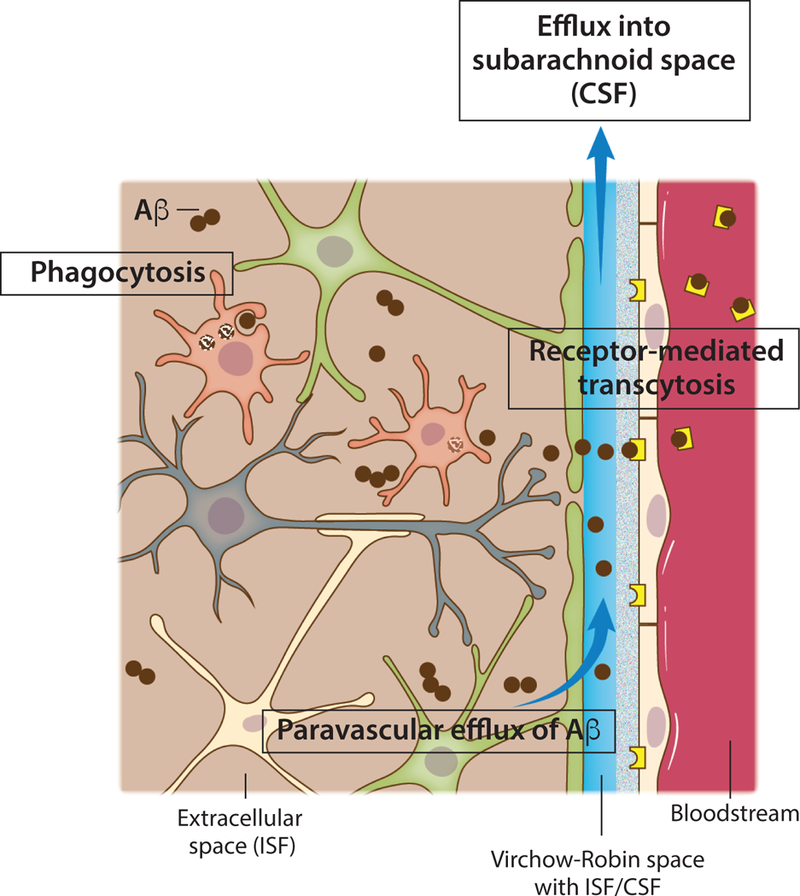
Toxic amyloid beta (Aβ) peptides are present in the extracellular brain ISF. One of the most important mechanisms of Aβ clearance from the brain extracellular environment is receptormediated transcytosis across the blood-brain barrier. Monomeric or aggregated Aβ can also be internalized and degraded by brain phagocytes, resident microglia or monocyte-derived macrophages that might be recruited and engraft the brain. Efflux of soluble Aβ from the brain ISF back into the subarachnoid CSF sink also takes place through paravascular spaces (glymphatic route).
