Figure 5.
EMC and Sec61 Complex Act at Different Steps during β1AR Insertion
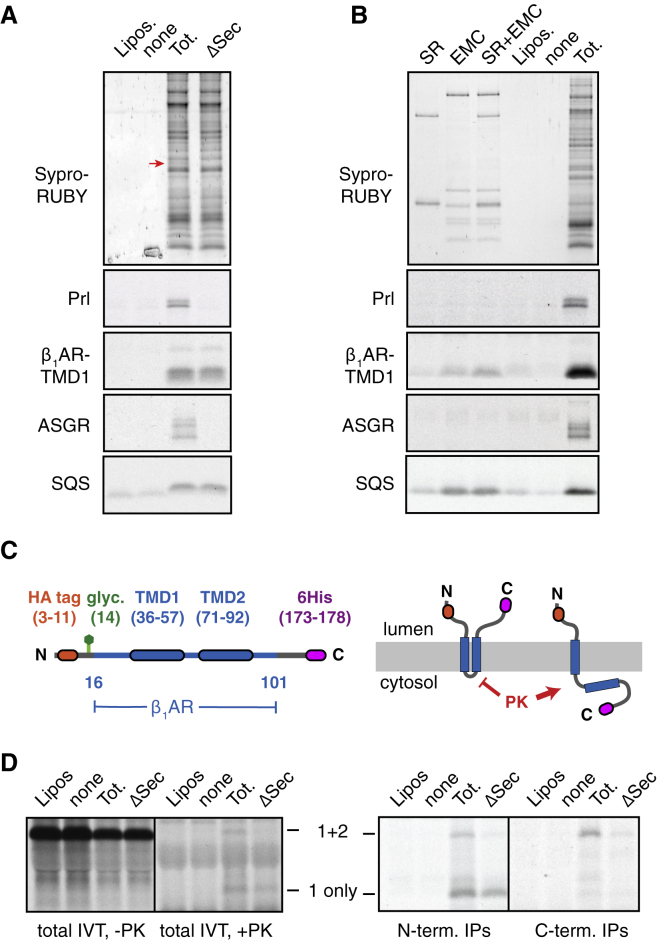
(A) The indicated constructs were analyzed by the protease-protection assay for translocation into liposomes (Lipos) or proteoliposomes reconstituted from total ER proteins (Tot.) or ER proteins immunodepleted of the Sec61 complex (ΔSec). Total proteins in the proteoliposomes were visualized by Sypro Ruby, with the position of Sec61α indicated by the red arrow. Depletion was verified to be over 95% (see Figure S6A). The remaining panels show protease-protected (and hence, translocated) products recovered by immunoprecipitation.
(B) The indicated constructs were analyzed by the protease-protection assay for translocation into liposomes (Lipos), proteoliposomes reconstituted from total ER proteins (Tot.), or proteoliposomes containing the indicated purified proteins (SR is SRP receptor). Proteins in the proteoliposomes were visualized by Sypro Ruby. 10-fold excess of the first four lanes were loaded to detect the purified proteins. EMC and SR did not contain any detectable Sec61 contamination (see Figure S6D). The remaining panels show protease-protected (and hence, translocated) products recovered by immunoprecipitation.
(C) Diagram of the two-TMD β1AR construct and its topology when TMD2 inserts or fails to insert into the membrane. Only the single-spanning form is accessible to proteinase K (PK) digestion (see Figure S7).
(D) The two-TMD construct from (C) was analyzed in the indicated proteoliposome preparations by the protease-protection assay. The left panel shows total products, while the right panel shows the PK-digested products after recovery via N- or C-terminal tags as indicated. “1+2” indicates the protected product indicative of the double-spanning topology, and “1 only” indicates the single-spanning topology.
See also Figures S6 and S7.