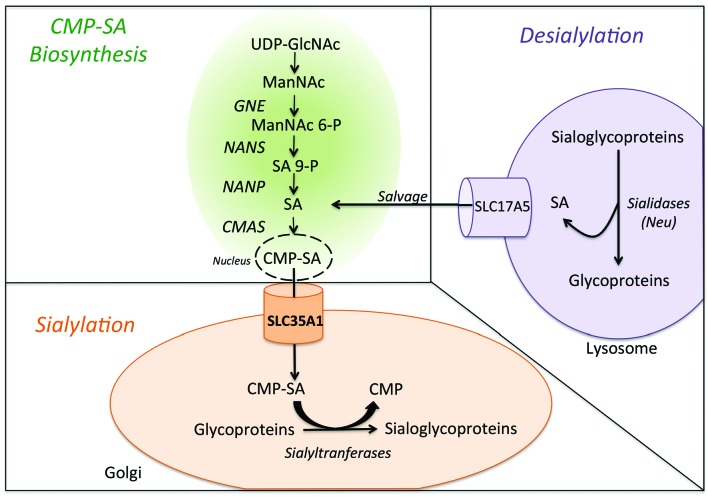
Figure 1.
A simplified diagram of sialic acid metabolism in human. Biosynthesis of sialic acid (SA) mostly takes place in the cytoplasm, although the CMP–sialic acid synthase (CMAS) reaction occurs in the nucleus. The synthesis of ManNAc (N-acetylmannosamine) is carried out in two steps by UDP-GLcNAc–2 epimerase (GNE). NeuNAc synthase (NANS) generates phosphorylated forms of sialic acid, which must be dephosphorylated by a specific phosphatase (Neu5Ac-9-P-phosphatase, NANP) to yield free sialic acid in the cytoplasm. The free sialic acid can then reenter the biosynthesis pathway (indicated as “salvage” in the diagram). The CMP-SA (produced in the nucleus) is transferred by SLC35A1 into the Golgi apparatus, where it is used as a substrate for sialylation by sialyltransferases.