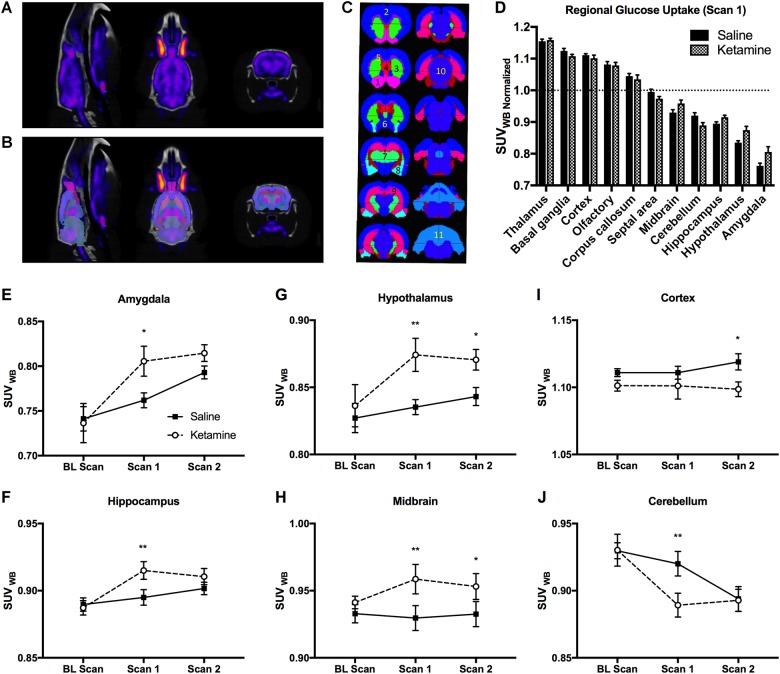
Fig. 4. The effects of IV ketamine infusion on BGluM of rats.
A Representative images of FDG-PET and CT of a rat brain (sagittal, planar, and coronal section, from left to right). B FDG-PET and CT images that are co-registered with the three-dimensional rat brain atlas. C Major brain regions quantified using the rat brain atlas. 1: Olfactory, 2: Cortex, 3: Basal Ganglia, 4: Septal Area, 5: Corpus Callosum, 6: Hypothalamus, 7: Thalamus, 8: Amygdala, 9: Hippocampus, 10: Midbrain, 11: Cerebellum. D IV Ketamine (10 mg/kg) infusion induced region-specific changes in BGluM as compared with the saline infusion. The IV Ketamine infusion (Scan 1) increased BGluM in the amygdala (E), hippocampus (F), hypothalamus (G), and midbrain (H), whereas decreasing it in the cerebellum (J). The fear memory testing (Scan 2) increased BGluM in the hypothalamus (G) and midbrain (H), whereas decreasing it in the cortex (I). SUV: standard uptake value. The SUV of each region was normalized with the SUV of the whole brain of the same animal. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. saline controls)