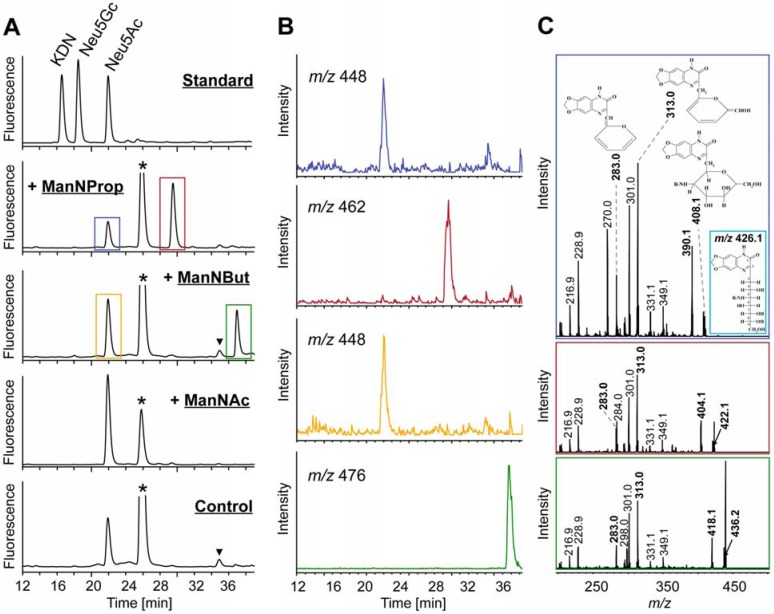
Figure 4.
Analysis of sialic acids present in whole cell lysate from HUVECs treated with peracetylated ManNProp, ManNBut, and ManNAc. (A) DMB-labeled sialic acid residues were separated by RP-HPLC. For control, HUVECs were not incubated with any sialic acid precursors. (B) EIC of sodium adducts ([M+Na]+) of Neu5Ac (m/z 448) and Neu5Prop (m/z 462) as well as Neu5Ac (m/z 448) and Neu5But (m/z 476) present in HUVECs incubated with peracetylated ManNProp and ManNBut, respectively. Peaks related to DMB reagent are labeled with an asterisk (*) and those related to further unidentified impurities are marked with a triangle (▼). (C) ESI-MS/MS analyses of Neu5Ac (upper profile), Neu5Prop (central profile) and Neu5But (lower profile) are registered as proton adducts ([M+H]+). For fragmentation analyses, respective parent ions generated after loss of water were selected. Annotation of fragment ions was performed according to the fragmentation pathway of DMB-labeled sialic acids proposed by Manzi and co-workers [12] with monoisotopic masses of respective fragment ions printed in bold. Corresponding structures of generated fragments are given exemplarily in the upper profile. For the structure of Neu5Ac (m/z 426.1) prior to loss of water see inset.