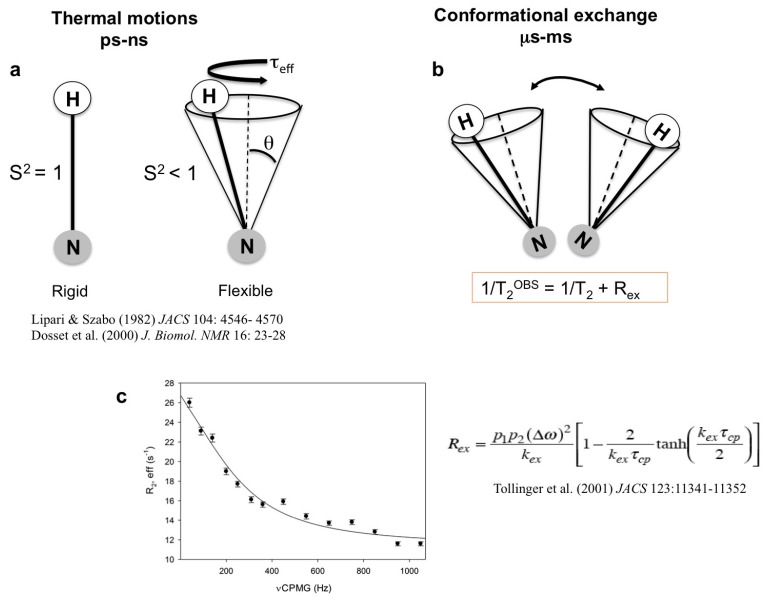
Figure 1.
The characterization of pico- to millisecond timescales using spin relaxation measurements can probe internal motions of the bond vector. Model-free analysis of relaxation data (longitudinal relaxation (R1) and transverse relaxation (R2)) yield an order parameter (S2) that describes the amplitude of motion, a constant (τeff) describing its timescale [37,38,39] (a) and Rex that describes the additional exchange contribution in R2 (b). A representative relaxation dispersion curve demonstrating the dependence of Rex that can be used to extract the populations (p), exchange rates (k) and chemical shifts (ω) of ground and exited states (see the equation) [40]. The curve was fitted using CPMGFit program (www.palmer.hs.columbia.edu) [41] (c).