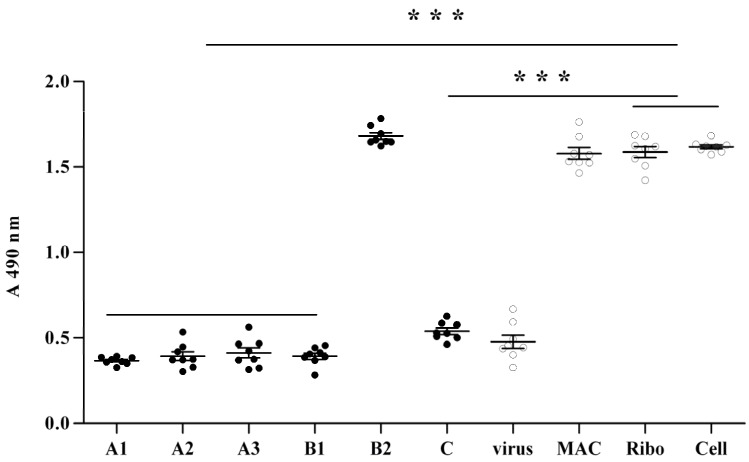
Figure 2.
Protection efficacy by MAC against 2009 H1N1 virus infection to MDCK cell.
A: 0.020% MAC was applied to the MDCK cell monolayer for 1 h (A1), 2 h (A2) and 4 h (A3), respectively. MAC in each MDCK cell culture was then removed by extensive sterile PBS wash and then 2009 H1N1 virus in 100 TCID50 were infected for 1 h and then instead of the maintenance media. B: MAC was diluted into 0.010% with the final concentration of 103 TCID 50/mL 2009 H1N1 virus suspension for incubation of 0.5 h and 1 h (B1 and B2), respectively. The mixtures were added to MDCK cells monolayer for 1 h and then replaced by maintenance media. C: 100 TCID50 influenza viruses were inoculated to a MDCK cell monolayer for 1 h. The supernatant was then replaced by 0.020% MAC/DMEM. Virus, MAC, ribo and cell represent 2009 H1N1 influenza virus control, 0.020% MAC control, 0.010% ribavirin anti the influenza virus control and the MDCK cell control, respectively. The viability of MDCK cells were then determined by MTT method when over level 2 CPE was observed in the virus control and the cell control showed no CPE (about 48 h). The data were presented as mean ± S.D. ***: p < 0.001.