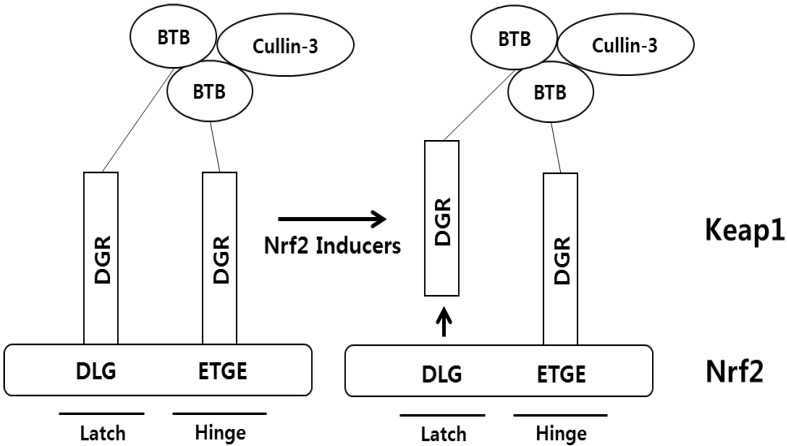
Figure 3.
The “Hinge and Latch” Hypothesis. Under basal conditions, Keap1 forms a homodimer and associates with Cullin-3 protein. At the same time, the DGR domains of two Keap1 bind to the DLG (latch) and the ETGE (hinge) domains in a single Nrf2. In response to Nrf2 inducers, the DLG motif in Nrf2, but not ETGE motif in Nrf2, is released from the DGR domain in Keap1.