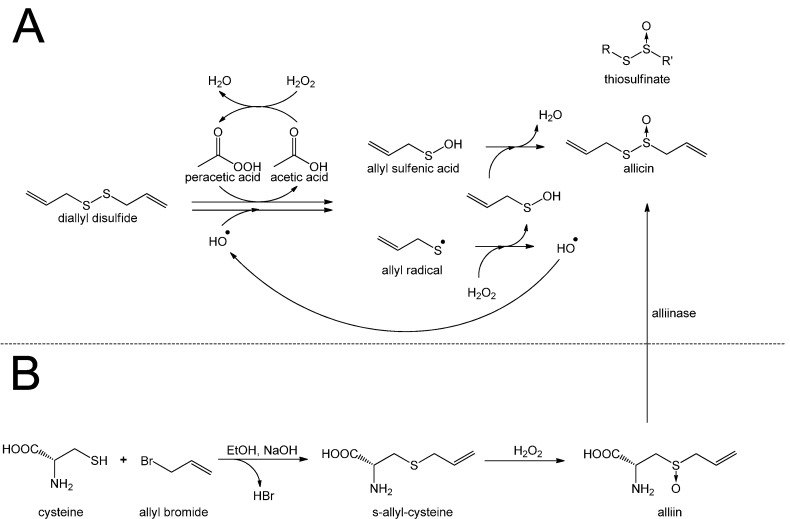
Scheme 2.
Synthesis of allicin according to Stoll and Seebeck: (A) Diallyl disulfide (distilled under reduced pressure) is mixed with acetic acid and hydrogen peroxide. Because hydrogen peroxide reacts very slowly with diallyl disulfide, acetic acid is needed as a catalyst. Peracetic acid (ethaneperoxoic acid) is formed, which is able to oxidize diallyl disulfide to allyl sulfenic acid. This reaction also leads to the production of allyl radicals which can react with hydrogen peroxide to form allyl sulfenic acid and hydroxyl radicals. The latter are able to react with diallyl disulfide to form allyl sulfenic acid and allyl radicals again. Two molecules of allyl sulfenic acid condense to allicin. This reaction mechanism is not only suitable to synthesize allicin but also other thiosulfinates. (B) To produce allicin by an enzymatic reaction alliin is needed. Cysteine is mixed with allyl bromide in an alkaline (NaOH) mixture of water and ethanol to obtain S-allyl cysteine. The latter can be oxidized with hydrogen peroxide to produce alliin. By an enzymatic reaction of alliin with alliinase, allicin is formed.