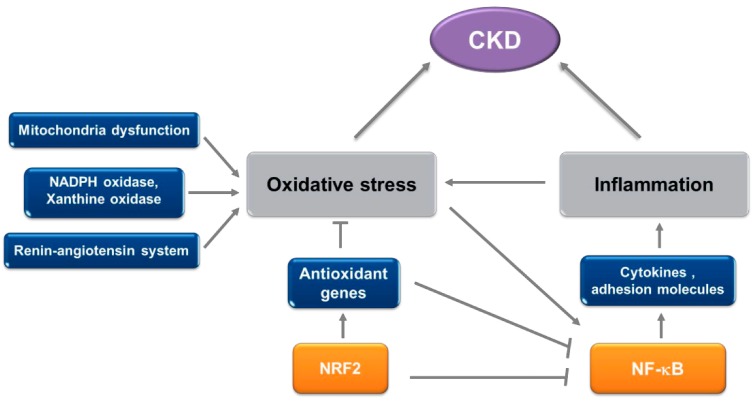
Figure 2.
Factors involved in the progression of kidney dysfunction in CKD and the role of NRF2. In CKD, the alteration of mitochondrial function and the activation of ROS-generating enzymes such as NADPH oxidase and xanthine oxidase participate in aggravated oxidative stress condition in the kidney. The activation of the renin-angiotensin system is another important contributing factor. In addition, oxidative stress triggers NF-κB activation and enhances inflammatory response, which is an important pathologic component of CKD. NRF2 provides renal cells with antioxidant potential by up-regulating an array of genes and consequently attenuates the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and adhesion molecules.