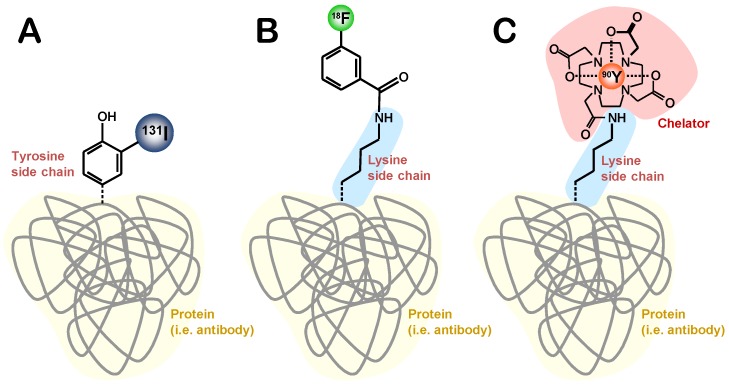
Figure 2.
Illustration of the three main strategies for the radiolabeling of proteins. (A) direct labeling (B) indirect labeling via a prostetic group and (C) indirect labeling via complexation. The different methods allow incorporating various types of radiolabels into a protein: (A) iodine (B) fluorine and (C) metallic radionuclides. Maleimides and other functionalities that specifically react with thiols are a common alternative to the use of radiolabeled synthons linked to lysine side chain amines shown in examples (B) and (C).