Table 1.
Characteristics of some bioreductive prodrugs [2].
| Prodrug | Chemical Structure | Chemical Class | Mechanism of Action * | Mechanism of Cytotoxicity | One-Electron Reductases | Two-Electron Reductases | KO2 (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPZ | 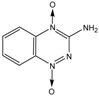 |
Aromatic N-oxide | 1, 3 [R.] *** | Complex DNA damage | CYPOR ** iNOS ** | NQO1 ** | ±1 |
| SN30000 | 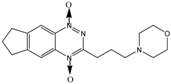 |
Aromatic N-oxide | 1, 3 [R.] *** | Complex DNA damage | CYPOR ** | ---- | ±1 |
| AQ4N | 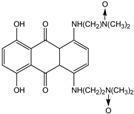 |
Aliphatic N-oxide | 2, 5 [Y] *** | Topoisomerase II inhibition | iNOS ** | CYP3A4 ** CYP2S1 ** | ---- |
| EP-0152R plus CB1954 | 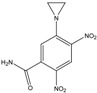 |
Nitro | 1/2, 4, 5, 6 [Y, Z] *** | DNA interstrand crosslink | CYPOR ** iNOS ** | NQO1 ** NQO2 ** | ---- |
| EO9 | 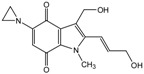 |
Quinone | 1, 4 [X, Y] *** | DNA interstrand crosslink | CYPOR ** | NQO1 ** | ---- |
* Reaction numbers: 1: one electron reduction generates a prodrug radical; 2: fragmentation of the prodrug radical generates radical R. and cytotoxin D; 3: one electron reduction of the prodrug radical; 4 and 5: subsequent reduction of the two electron reduction produces X; 6: two-electron reduction of the prodrug generates product X; ** CYPOR-NADPH–cytochrome P450 reductase, iNOS-inducible nitric oxide synthase, NQO-NAD(P)H dehydrogenase [quinone], CYP-cytochrome P 450; *** Active cytotoxins (R·, X, Y, Z). All abbreviations refer to reference [2] Figure 2A.
