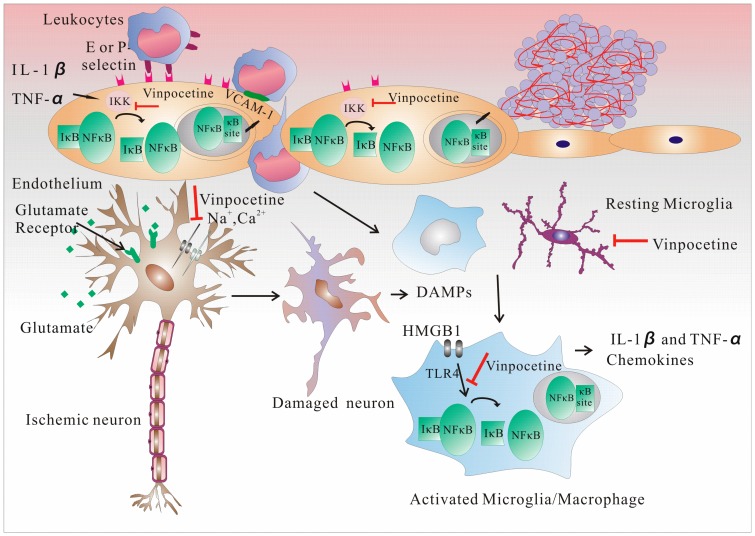
Figure 3.
Vinpocetine inhibits the progression of stroke through the inhibition of IKK/NF-κB. Vinpocetine inhibits the expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and the E- and P-selectins through the inhibition of nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells κB (NF-κB) in endothelial cells. This action protects the blood-brain barrier and reduces blood leukocyte attraction and recruitment. Vinpocetine protects neurons by inhibiting voltage-sensitive sodium channels and inhibiting cellular Ca2+ accumulation, which can lead to cell swelling and damage. Damaged neurons release danger-associated molecular patterns, which activate microglia and macrophages through Toll-like receptor 4 activation in the NF-κB pathway. Vinpocetine hinders this process by inhibiting inflammatory cytokine release and magnification. Although vinpocetine does not affect the activation of microglia, it inhibits the proliferation of microglia through NF-κB and the activator protein-1 transcription factors, which are major transcription factors that regulate the genes responsible for both the innate and adaptive immune responses and are important in the differentiation of T cells.