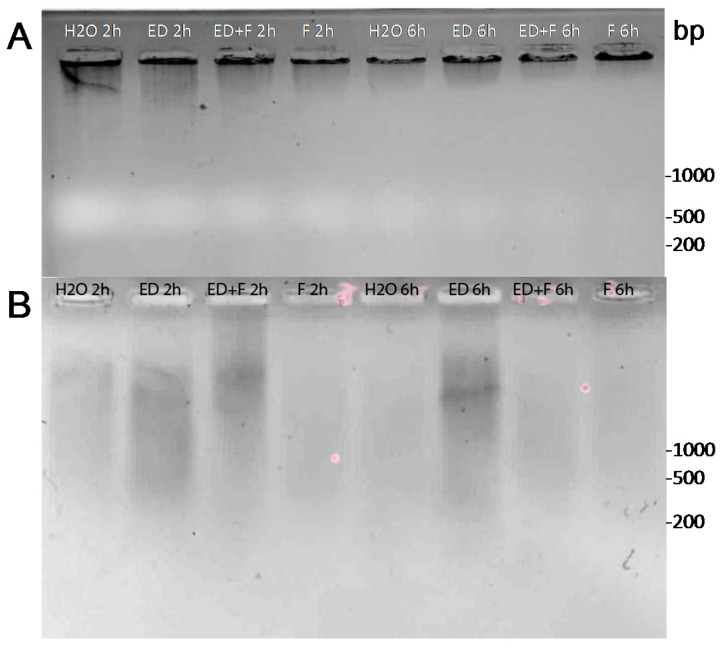
Figure 4.
EDTA applications to pea endocarp tissue result in fragmentation of DNA in the period disease resistance is initiated (1–6 h). DNA was extracted from pea endocarp tissue (A) treated for 2 h and 6 h with (10 μL) water (H2O), 6 mM EDTA (ED), 6 mM EDTA + Fusarium solani f. sp. phaseoli spores (ED + F) or F. solani spores only (F). DNA (2 µg of each treatment was loaded per well) was separated on 1% agarose gels. The fragmented DNA was further separated from the bulk of the high molecular pea DNA (25 µg) by agarose retention disks under alkaline conditions (B) and the diffused fragmented DNA from the agarose disk recovered and separated on standard agarose gels. (Photos are inverted images of ethidium bromide stained DNA).