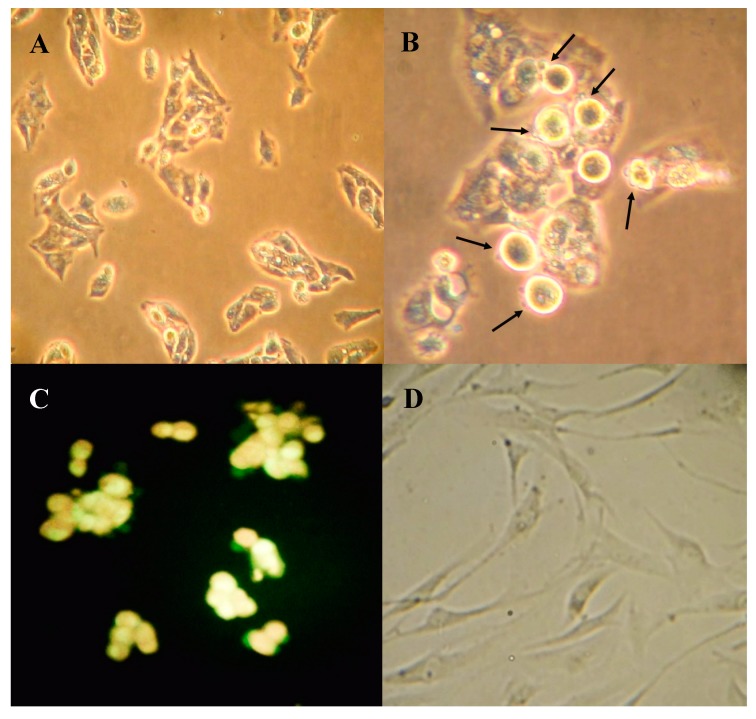
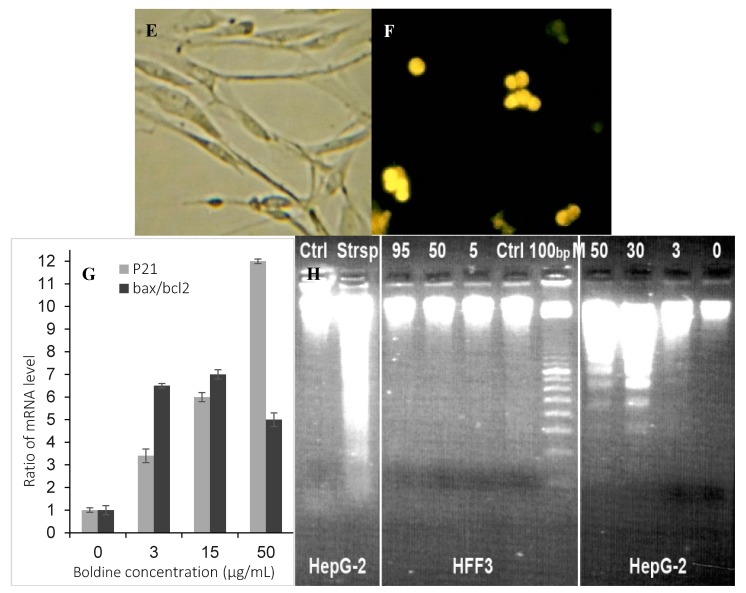
Figure 4.
HepG-2 and HFF cells seeded on cover slip (A and D respectively) and treated with 50 µg/mL boldine for 48 h (B and E respectively), fixed and viewed with inverted phase microscope. Fluorescence microscopy after staining with acridine orange and ethidium bromide (C and F respectively). The magnification is 200× in A and D, E, F and 400× in B and C. Relative expression of p21 p < 0.01, and bax/bxl2 in HepG-2 cells treated with boldine for 48 h; p < 0.02 (G). Apoptotic DNA fragmentation in HepG-2 cells after boldine treatment (from right to left: 0 (untreated control), 3, 30, 50 µg/mL, respectively) separated in agarose gel electrophoresis. HFF3 treated with 0, 5, 50 and 95 µg/mL showed no DNA fragmentation. DNA sample from HepG2 cells treated with staurosporin as a known apoptosis inducing compound and untreated cells, respectively (H).