Table 1.
Anti-HCV activities and cytotoxic effects of quercetin-7-O-substituted derivatives.
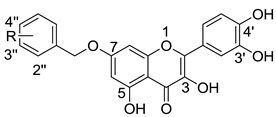
| Compound | R | EC50(μM) a,b,c | CC50(μM) c,d | SI e | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | Substituent | ||||
| 3a | - | H | 8.7 ± 0.2 | >50 | >5.8 |
| 3b | 2'' | F | 5.0 ± 0.1 | 15.4 ± 0.1 | 3.1 |
| 3c | Cl | 4.8 ± 0.1 | 36.7 ± 0.7 | 7.7 | |
| 3d | Br | 5.5 ± 0.2 | 37.4 ± 0.8 | 6.8 | |
| 3e | CH3 | 4.9 ± 0.6 | 21.7 ± 1.4 | 4.4 | |
| 3f | CN | 7.5 ± 0.5 | 12.6 ± 0.1 | 1.7 | |
| 3g | NO2 | 7.0 ± 1.1 | 14.6 ± 0.5 | 2.1 | |
| 3h | 3'' | F | 6.3 ± 0.2 | 44.5 ± 3.7 | 7.7 |
| 3i | Cl | 3.8 ± 0.2 | 27.2 ± 0.2 | 7.2 | |
| 3j | Br | 4.1 ± 0.3 | 22.3 ± 1.2 | 5.4 | |
| 3k | CH3 | 4.7 ± 0.4 | 32.5 ± 0.7 | 6.9 | |
| 3l | CN | 5.4 ± 0.5 | 10.6 ± 0.5 | 2.0 | |
| 3m | NO2 | 6.6 ± 1.1 | 15.0 ± 0.1 | 2.3 | |
| 3n | 4'' | F | 5.1 ± 0.5 | 31.9 ± 3.4 | 6.2 |
| 3o | Cl | 3.9 ± 0.3 | 15.1 ± 0.1 | 3.9 | |
| 3p | Br | 5.5 ± 1.5 | 35.4 ± 1.6 | 6.4 | |
| 3q | CH3 | 6.7 ± 1.4 | 15.9 ± 1.0 | 2.4 | |
| 3r | CN | 6.2 ± 0.2 | 10.1 ± 0.1 | 1.6 | |
| 3s | NO2 | 4.3 ± 0.2 | 19.6 ± 0.2 | 4.5 | |
| 2 | quercetin | 19.8 | >50 | >2.5 | |
a The anti-HCV assay was evaluated in an authentic HCV infection system in the human hepatoma cell lines, Huh7.5.1; b Concentration required to inhibit HCV RNA replication by 50%; c The values obtained as the average of duplicate determinations; d Concentration required to reduce cell proliferation by 50%; e Selectivity index: ratio of CC50 to EC50.
