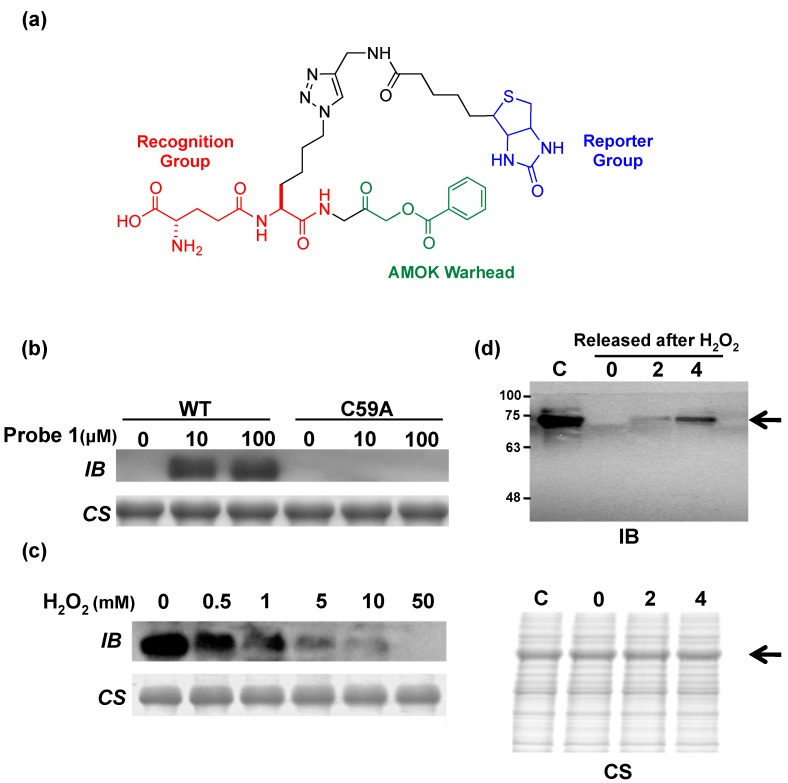
Figure 5.
(a) Structure of an acyloxymethyl ketone (AOMK) activity-based probe (ABP) for the characterization of Gsp amidase in E. coli [49]. A typical ABP includes a warhead for covalent crosslinking (in color green), a domain to enhance binding selectivity (red), and a reporter group to allow for experimental characterization (blue); (b) Recombinant Gsp synthetase/amidase (GspSA, “WT”) and the mutant C59A could be distinguished by immunoblotting; (c) The extent of GspSA deactivation by H2O2 could be differentially assayed; (d) GspSA could be specifically identified in vivo. Upon peroxide treatment, the amount of active Gsp amidase in E. coli cultures could be measured. The arrow identifies the expected position of GspSA (MW of 70 kDa). WT: wild-type GspSA; IB: immunoblotting using anti-biotin; CS: Coomassie Blue staining; C: negative control, no H2O2 treatment. Lanes marked 0, 2, 4, denote the duration of recovery (h) after H2O2 release [49]. © Wiley-VCH.