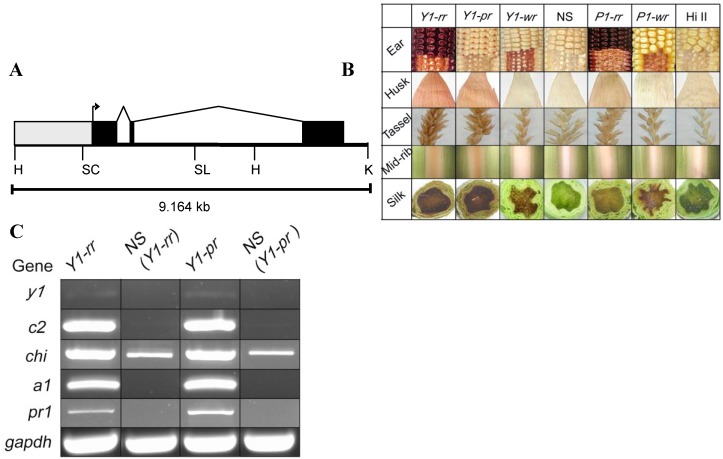
Figure 2.
Characterization of y1 transgenes. (A) Structural features of the sorghum y1 gene. The gray box represents the upstream regulatory region. The bent arrow indicates the transcription start site. Solid boxes correspond to exons that are joined by angled lines representing introns. The restriction enzyme sites shown are: H, HindIII; K, KpnI; SL, SalI; SC, ScaI. Illustration not drawn to scale. (B) Sorghum y1 gene-induced pigmentation phenotypes in transgenic Y1-maize. Three y1 transgenic events representing Y1-rr, Y1-pr and Y1-wr were characterized for ear, husk, tassel glumes, leaf mid-rib, and silk browning phenotypes. Comparable controls included are: plants segregating for the absence of y1 transgene shown as negative segregant (NS) and native p1 expressing alleles P1-rr and P1-wr and HII (from A188 X B73), used for transformation. (C) Sorghum y1 gene induces flavonoid structural genes in Y1-maize. The expression of the y1 transgene and four flavonoid structural genes relative to the housekeeping gene glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase was assayed using RT-PCR. Expression was tested in the pericarp tissues of the Y1-rr and Y1-pr transgenes and their respective negative segregants (Y1-rr and Y1-pr). c2: chalcone synthase, chi: chalcone isomerase, a1: dihydroflavonol reductase, pr1: flavonoid 3'-hydroxylase, gapdh: glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase.