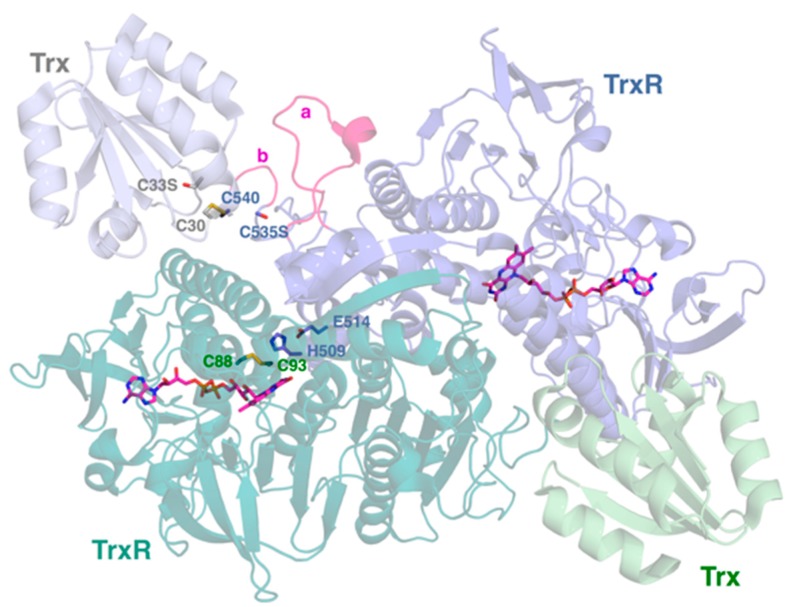
Figure 1.
The dimeric structure of P. falciparum thioredoxin reductase (TrxR). The two subunits of TrxR are shown with their bound FAD cofactors in magenta. The redox active disulfide (C88–C93) of the N-terminal redox center is shown for the TrxR monomer on the lower left. H509 and E514 that modulate the reactivity of this N-terminal redox center are supplied by the TrxR monomer on the upper right. Each monomer is bound to substrate Trx via intermolecular disulfide (TrxR C540 to Trx C30). The positions of C535 (TrxR) and C33 (Trx) are indicated by serine residues. These substitutions were made in order to trap the intermolecular disulfide between TrxR and Trx [23]. The 535 and 540 residues shown are supplied by the TrxR monomer on the upper right. The Plasmodium-unique insertions H438–S452 and G536–K539 are highlighted by a and b, respectively. Coordinates are drawn from PDB accession 4J56 [23]. The figure was generated using PyMOL 1.6.0.0.