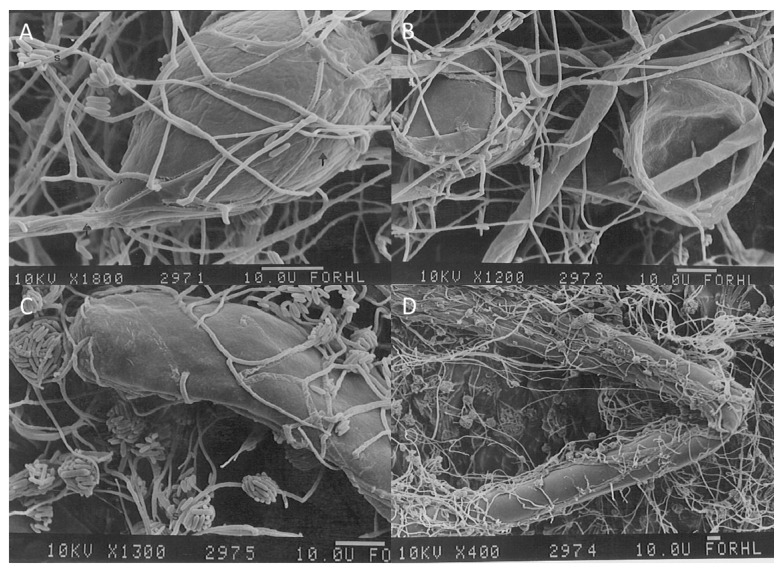
Figure 8.
Top (A) Intermediate mycoparasitic stage of L. muscarium against Phytophtora palmivora: arrows show the contact between the thin mycelium of the Antarctic fungus and a P. palmivora sporangium; s = spores of L. muscarium. (B) Late mycoparasitic stage of L. muscarium against P. palmivora; the oomycete appeared completely overwhelmed by the fungus. Bottom. (C) Intermediate mycoparasitic stage of L. muscarium against Mucor mucedo: the Antarctic fungus (thin mycelium) establishes firm contact with the host (thick mycelium) and penetrates it. (D) Late mycoparasitic stage of L. muscarium against M. mucedo: the host appears completely overwhelmed. Extensive sporulation of L. muscarium is always recorded (modified from [19]).