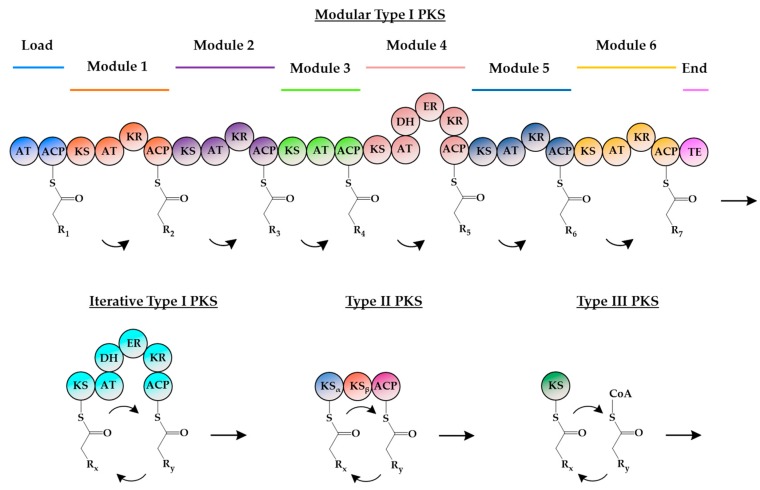
Figure 2.
Domain organization of the different PKSs. Putative domains are represented by circles. In modular type I PKSs, functional domains are organized into several modules, with each module being responsible for a single decarboxylative condensation step in polyketide formation. For iterative type I PKSs, the functional domains are clustered in a single module, and each domain is used repeatedly during polyketide synthesis. Type II PKSs are dissociable multi-enzyme complexes, with each protein bearing a single and independent catalytic domain that is used iteratively during polyketide formation. Reactions by type III PKSs are also iterative but do not require an ACP for the attachment of the growing polyketide chain. AT: Acyltransferase; ACP: Acyl carrier protein; KS: Ketosynthase; KR: Ketoreductase; DH: Dehydratase; ER: Enoyl reductase; TE: Thioesterase; CoA: Coenzyme A.