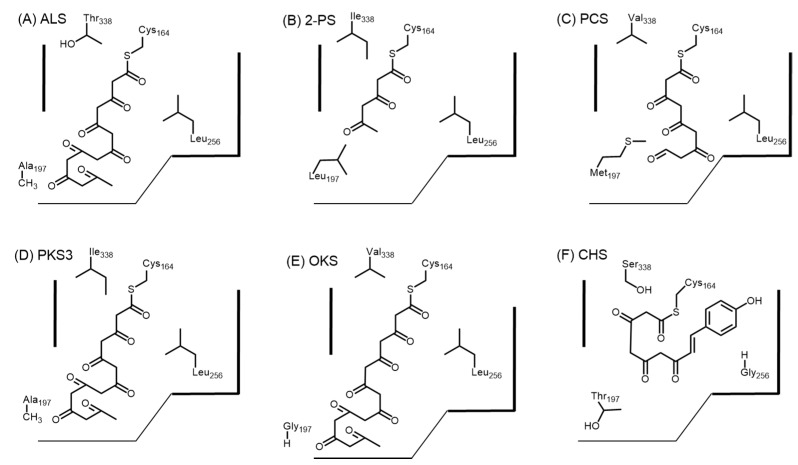
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of the active sites of (A) R. Palmatum ALS; (B) G. hybrida 2-PS; (C) A. arborescens PCS; (D) A. arborescens PKS3; (E) A. arborescens OKS; and (F) M. sativa CHS. The residue at position 256 controls the starter unit selectivity. Bulky residues such as leucine prevents the entrance of starter acyl-CoAs such as p-coumaroyl CoA. The residue at position 197 controls the gate to an additional buried pocket that extends to the “floor” of the active site. Small residues such as alanine or glycine allows chain extension to form octaketides. Residue at position 338 located at the proximity of the catalytic Cys164 is at the “ceiling” of the active site cavity and this guides the growing polyketide chain to extend into the buried pocket near residue position 197. The numbering for all enzymes are based in M. sativa CHS.