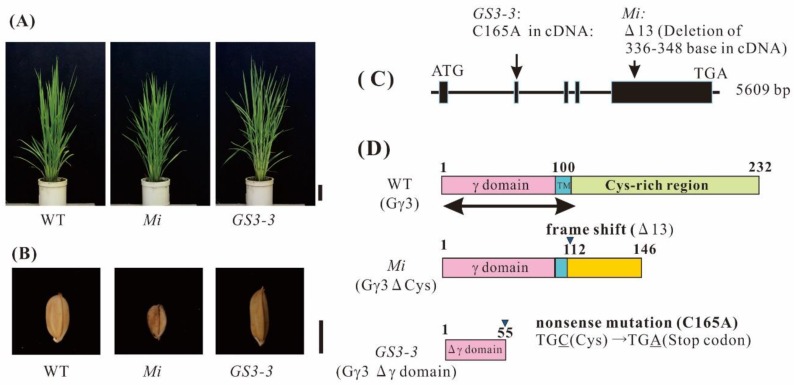
Figure 1.
Morphology of rice heterotrimeric G protein γ3 gene (RGG3/GS3/Mi/OsGGC1) mutants, and genome and protein structure of RGG3/GS3/Mi/OsGGC1. (A) Gross morphology of the wild-type (WT) (Taichung 65), Mi and GS3-3; Bar = 10 cm. (B) Seed morphologies of the plants in (A); Bar = 5 mm. (C) Genome structure of RGG3/GS3/Mi/OsGGC1 and positions of mutations in RGG3/GS3/Mi/OsGGC1 mutants, Mi and GS3-3. The 13-base deletion (336–348th base in full-length cDNA) and one base substitution (C165A in full-length cDNA) had occurred in Mi and GS3-3, respectively. In GS3-3, a codon, TGC (cysteine) changed to TGA (stop codon). (D) Protein structure of the product of RGG3/GS3/Mi/OsGGC1 in the WT (Gγ3), Mi (Gγ3ΔCys), and GS3-3 (Gγ3Δγ domain). The canonical γ domain region is shown as γ domain (pink bar). The putative transmembrane domain is indicated as TM (blue bar). The region with cysteine abundance is labeled as cysteine-rich region (green bar). The newly produced amino acid sequence by the frame shift resulting from of 13-base deletion is indicated with a yellow bar. An arrow under the WT Gγ3, which covers 120 amino acid residues from N-terminal, is the region used for recombinant proteins, such as the thioredoxin (Trx)-tagged Gγ3 domain protein (Trx-Gγ3 domain protein), used as an antigen, and the glutathione S transferase (GST)-tagged Gγ3 domain protein (GST-Gγ3 domain protein), used for affinity purification of the antibody.