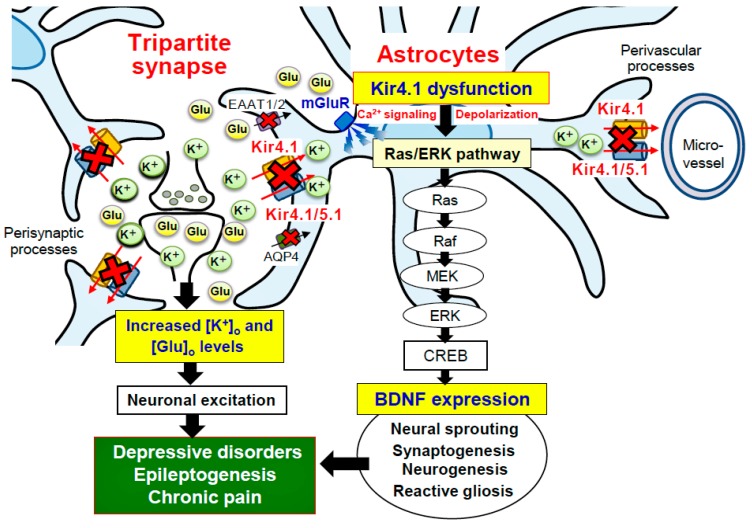
Figure 6.
Schematic diagram showing the effects of Kir4.1 inhibition on neuronal excitability and astrocytic BDNF expression. Inhibition (e.g., gene mutation, reduced expression, and pharmacological blockade) of Kir4.1 channels increases the [K+]o and [Glu]o levels at synapses and elevates neural excitability. Kir4.1 inhibition also activates the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway and enhances BDNF expression in astrocytes, facilitating neural sprouting, synaptogenesis, neurogenesis and reactive gliosis. Through these influences, Kir4.1-containnng channels seem to play crucial roles in modulating the development of central nervous system disorders such as epilepsy and mood disorders (e.g., major depression).