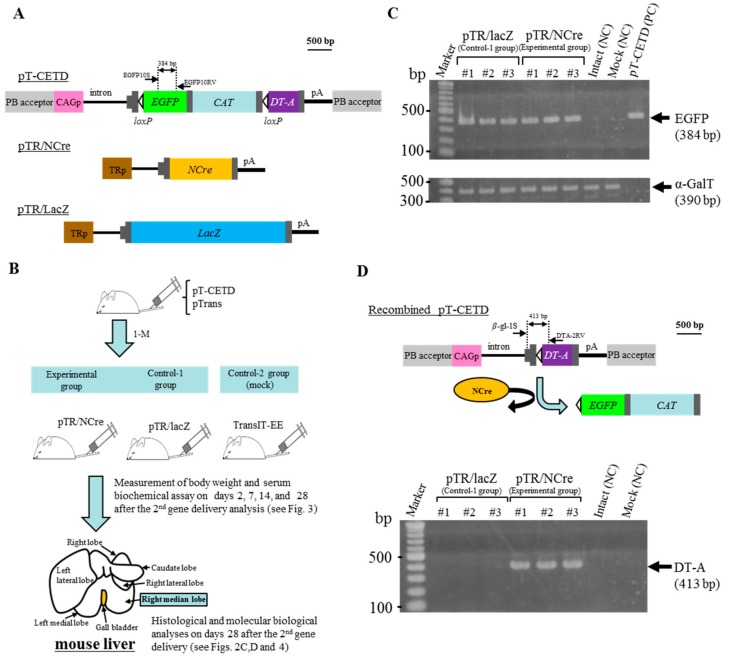
Figure 2.
Hydrodynamics-based gene delivery and PB transposon system enable the creation of disease models for liver dysfunction. (A) Structure of plasmid vectors used for the creation of liver disease model mice. The position of primers is shown above each plasmid; (B) Schematic representation of experimental outline for the creation of mice with liver dysfunction. Adult ICR males are first subjected to HGD with a solution containing pT-CETD and pTrans. One month later, they are then subjected to the second HGD with a solution containing pTR/NCre (experimental group) or pTR/lacZ (control-1 group). Males are also mock-injected as control-2 group. After the second gene delivery and mock injection, blood is collected from these mice on the indicated days. Twenty-eight days after the second gene delivery and mock injection, mice are subjected to blood collection and then sacrificed to dissect their liver (right median lobe) for pathological and molecular biological analyses; (C) PCR analysis of genomic DNA isolated from the HGD-treated males in the experimental and control-1 groups. For each group, three females (#1 to #3) were analyzed. Genomic DNA (approximately 5 ng) was PCR-amplified using primers recognizing EGFP cDNA in pT-EGFP. Simultaneously, the same amounts of DNA were PCR-amplified using primers for detection of the endogenous α-GalT gene and used as internal controls. Intact (NC), genomic DNA from intact mouse liver used as a negative control; Mock (NC), genomic DNA isolated from mice in the control-2 group; PC, plasmid pT-CETD (5 ng) used as positive controls for EGFP cDNA sequence. Marker, 100-bp ladder markers; (D) Structure of pT-CETD after Cre-mediated recombination (upper panel) and PCR analysis of genomic DNA isolated from the females in the experimental and control-1 groups 28 days after the second gene delivery (lower panel). As shown in the upper panel, Cre protein provided from pTR/NCre acts to remove the loxP-flanked sequences in pT-CETD and finally allows the DT-A gene to be expressed by the upstream CAG. The DT-A gene after recombination can be detected by PCR using β-gl-1S and DTA-2RV primer set, as shown in the upper panel. Intact (NC), genomic DNA from intact mouse liver used as a negative control; Mock (NC), genomic DNA isolated from mice in the control-2 group. Marker, 100-bp ladder markers.