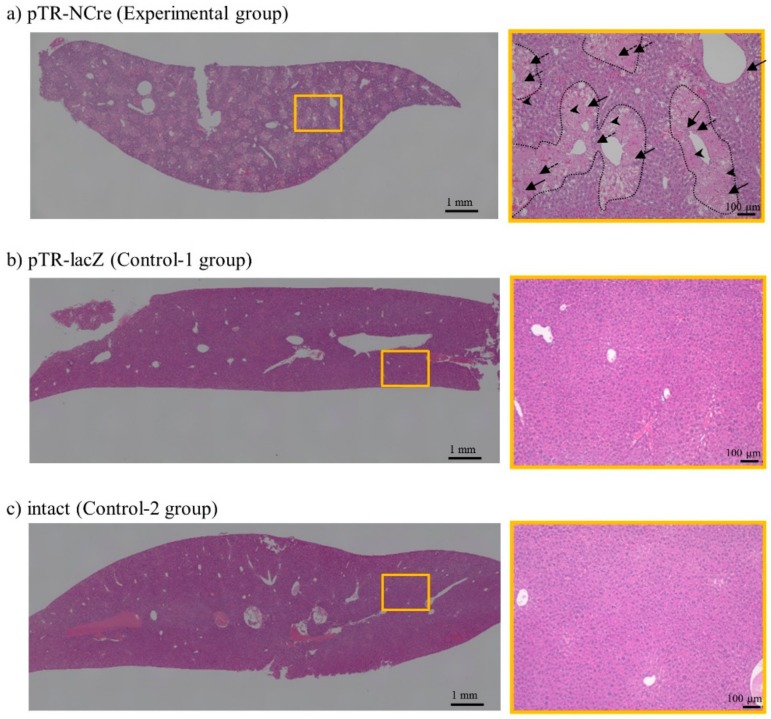
Figure 4.
Hydrodynamics-based gene delivery and PB transposon system enable the creation of disease models for liver dysfunction. Pathological analysis of the pT-CETD-incorporated females assayed 28 days after the second HGD with pTR/NCre (experimental group) or pTR/lacZ (control-1 group). These data are representative of three animals. Left panels, low-magnification images of dissected liver from mice (#1) in the experimental (a), and control-1 (b), and -2 groups (c). Abnormality was remarkable throughout the entire lobe in the experimental group. In contrast, liver in the control-1 and -2 groups remained normal. Right panels, images highly magnified from the boxes in the experimental (a), and control-1 (b), and -2 groups (c) shown in the left panels. Note the mixture of necrotic and intact areas in the experimental group (a). In particular, focal necrosis (enclosed by dotted lines) and inflammation were remarkable. Representative lymph corpuscle, enlarged Kupffer cells, and eosinophil granulocyte are shown by arrows, dotted arrows and arrowheads, respectively. The necrotic portion was more eosinophilic and enlarged.