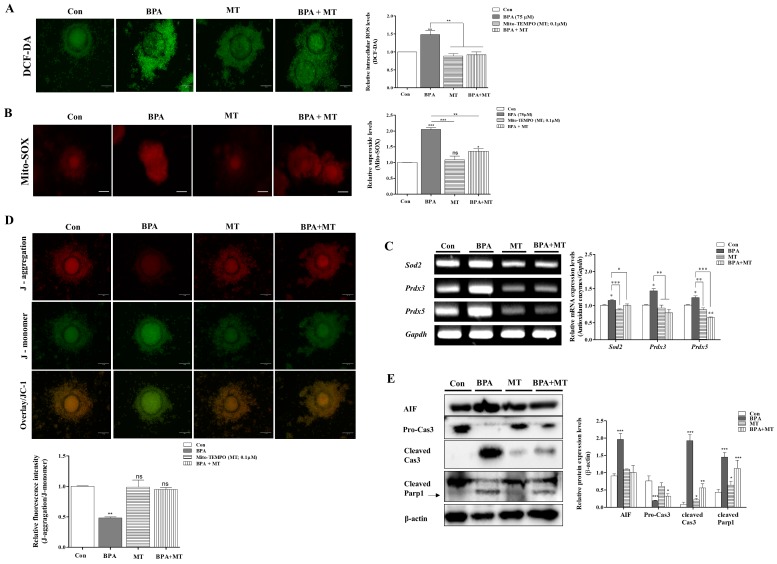
Figure 4.
Positive effects of Mito-TEMPO (MT) response to BPA-induced ROS production, mitochondria dysfunction, and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in mature porcine COCs. (A) Detection of intracellular ROS levels using DCF-DA staining in porcine COCs after BPA (75 μM) and/or MT (0.1 μM) treatment, respectively. (B) Identification of mitochondria-specific superoxide by Mito-SOX staining in matured COCs of BPA- and/or MT-treated groups. COCs from the treated groups were stained with Mito-SOX (red fluorescence) using the iRiS™ Digital Cell Image System (Logos Biosystems, Gyeonggi-do, Korea). Scale bar = 100 µm. (C) The mRNA levels of mitochondria-related antioxidant enzymes (Sod2, Prdx3, and Prdx5) in maturing porcine COCs from BPA-and/or MT-treated groups were measured using RT-PCR. (D) Measurement of MMP by JC-1 staining in matured COCs after BPA and/or MT treatment. COCs from treated groups were stained with JC-1 to evaluate MMP (Δψm) using the iRiS™ Digital Cell Image System (Korea). Scale bar = 100 µm. (E) Western blotting results of AIF, Pro-Cas3, cleaved Cas3 and cleaved Parp1 in BPA- and/or MT-treated porcine COCs as compared to the control. Relative folds of mitochondria-mediated apoptosis protein levels were obtained by normalizing the signals to β-actin. Histograms represent the values of densitometry analysis obtained using ImageJ software. Data in the bar graph are presented as the means ± SEM of three independent experiments (per 30 COCs). Differences were considered to be significant at * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, ***; p < 0.001 compared to control group.