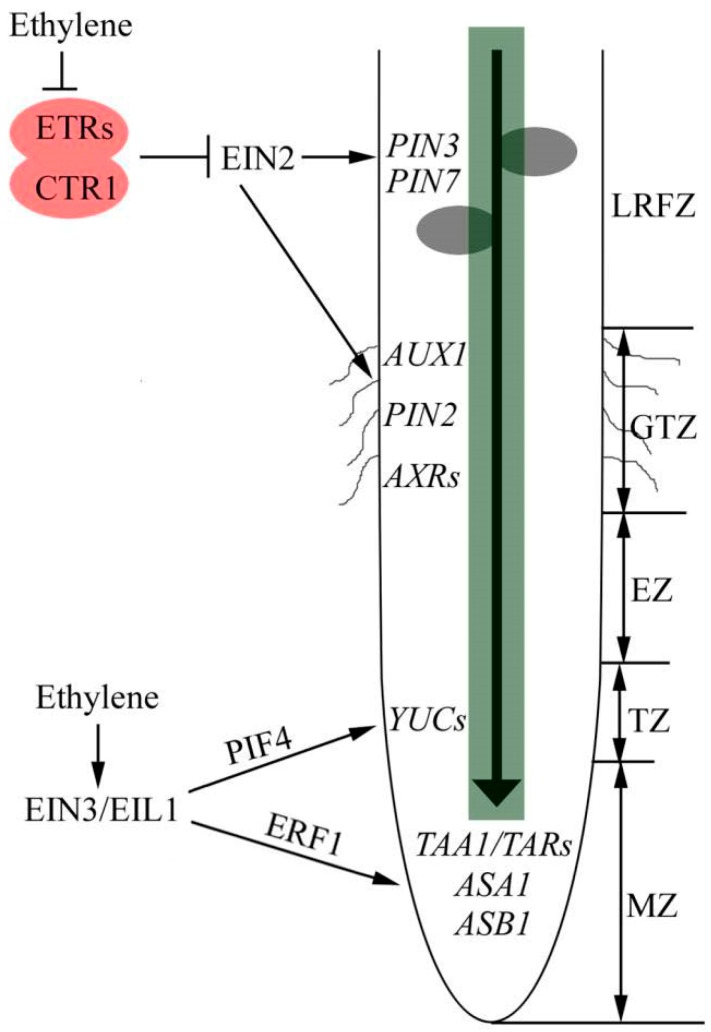
Figure 1.
Ethylene directs auxin to control root growth. The growth zones in root apex, including meristematic zone (MZ), transition zone (TZ), elongation zone (EZ) and growth terminating zone (GTZ). Ethylene promotes auxin biosynthesis in MZ and TZ through ASA1, ASB1, TAA1/TARs and YUCs, leading to inhibition of primary root elongation. ERF1 and PIF4 function as crosstalk nodes between ethylene and auxin in this process. In GTZ, ethylene promotes root hair initiation through modulation of the auxin levels mediated by auxin transporters. In the lateral root-forming zone (LRFZ), ethylene increases rootward auxin transport by increasing transcription and translation of PIN3 and PIN7 in the central cylinder, which prevent the localized accumulation of auxin needed to drive lateral root formation. Arrows indicates positive regulation, T sharp symbol indicates negative regulation, and waves in GTZ zone represent root hairs.