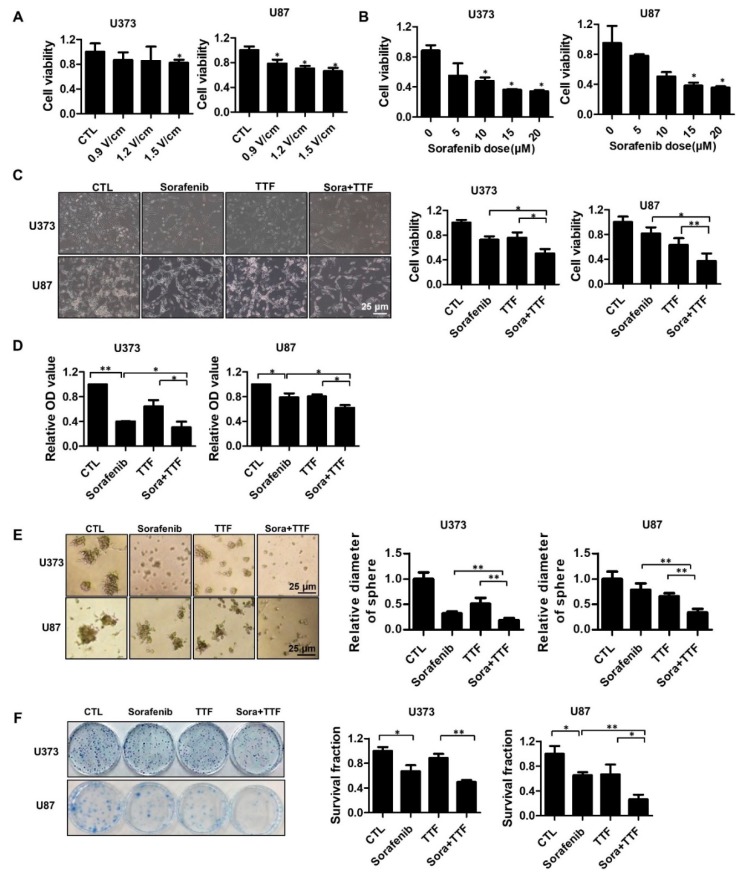
Figure 1.
Tumor-treating field (TTField)-sensitizing effects of sorafenib on in vitro models of glioblastoma. (A) TTFields inhibited glioblastoma cell viability in an intensity-dependent manner. Cell viability was evaluated by cell counting using 0.4% Trypan Blue stain for U373 and U87 cells treated with TTFields for the indicated durations; * p < 0.05; (B) sorafenib inhibited glioblastoma cell Fluorine-18viability in a dose-dependent manner. Cell viability was evaluated by cell counting using 0.4% Trypan Blue stain for U373 and U87 cells treated with the indicated doses of sorafenib; * p < 0.05. (C–E) the viability of cells treated with a combination of TTFields and sorafenib was significantly lower than that of cells treated with either sorafenib or TTFields. The proliferation rate was detected by counting (C), MTT assay (D), and 3D colony culture (E). * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; (F) the sensitivity of U373 and U87 cells treated with sorafenib and TTFields was measured via a colony formation assay. The survival fraction, which was expressed as a function of the irradiation dose, was calculated as follows: survival fraction = colonies counted/(cells seeded × plating efficiency/100). * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01. CTL: Control group; TTF: Tumor treating fields group.