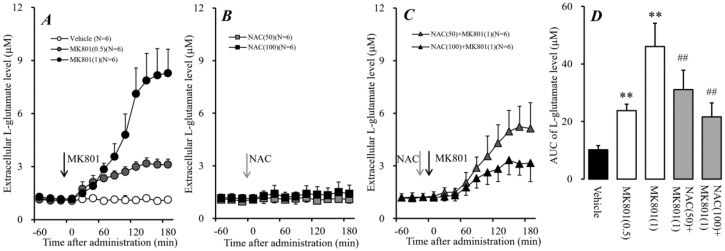
Figure 1.
Effects of 5-methyl-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d] cyclohepten-5,10-imine (MK801) and N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) on extracellular L-glutamate in the medial pre-frontal cortex (mPFC). (A) indicates the effects of systemic administration of MK801 (0.5 and 1 mg/kg, i.p.) on L-glutamate release in the mPFC. (B) indicates the effects of systemic administration of NAC (50 and 100 mg/kg, i.p.) on L-glutamate release in the mPFC, compared with the vehicle from (A). (C) indicates the effect of NAC (50 and 100 mg/kg, ip) on systemic MK801-evoked L-glutamate release in the mPFC, compared with MK801 alone (1 mg/kg, i.p.) from (A). Black and gray arrows indicate the intraperitoneal injection of MK801 and NAC, respectively. Microdialysis was conducted to measure the L-glutamate release in the mPFC. In (A–C), ordinates: mean ± SD (n = 6) of extracellular L-glutamate level in the mPFC (μM), abscissa: time after administration of MK801 (0.5 and 1 mg/kg) or NAC (50 and 100 mg/kg) (min). (D) indicates the area under curve (AUC) value of extracellular L-glutamate level in the mPFC (μM) after drug injection from 0 to 180 min of (A–C). ** p < 0.01; relative to vehicle (black) and ## p < 0.01; relative to MK801 (1 mg/kg, i.p.) (open) using the linear mixed effect model (LMM) with Tukey’s post hoc test.