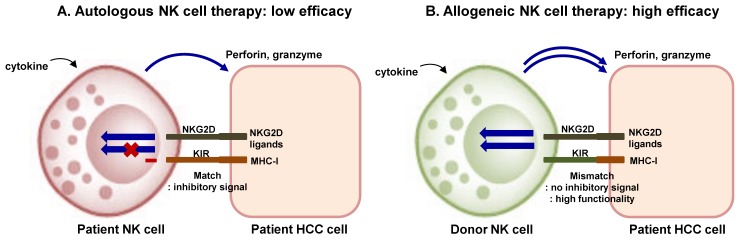
Figure 2.
Adoptive transfer of NK cells: Autologous and allogeneic NK cell transfer. (A) In autologous NK cell transfer, anti-tumor activity of NK cells might be limited by the inhibitory signal transmitted by the complex of matched KIR and self MHC class I molecule. (B) In allogeneic NK cell transfer, high cytotoxic responses can be obtained when donor NK cells do not express KIRs matching the MHC class I molecules of the tumor cells. KIR–ligand incompatibility is critical in efficacy of allogeneic NK cell therapy because the mismatch prevents the generation of negative signal and guarantees adequate NK cell activation. NK, natural killer cell; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; KIR, killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor; NKG2D, natural killer group 2 member D; MHC-I, major histocompatibility complex class 1.