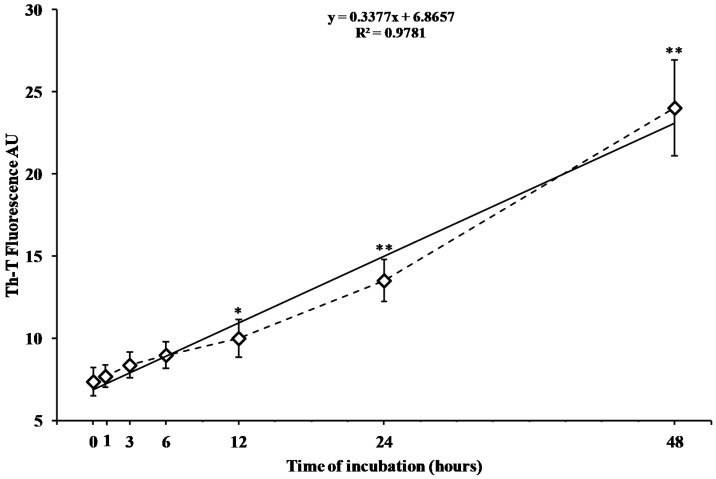
Figure 1.
Change in the fluorescence intensity of the Th-T assay caused by the aggregation of the peptide fragment hA17–29. The peptide fragment hA17–29 (100 µM) was incubated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4, at 37 °C for different times (0, 1, 3, 6, 12, 24, and 48 h). Fluorescence was monitored as a function of time in a 96-well plate using a microplate reader (LabSystems-Multiskan Ascent 354 Microplate Reader, San Diego, CA, USA). The fluorescence intensity was measured at 450 nm wavelength excitation/482 nm wavelength emission after 10 min of incubation of Th-T (3 µM) with the peptide fragment. The final fluorescence values were calculated by subtracting the fluorescence produced by control solutions (Th-T alone and aggregates in solution in absence of Th-T). Data are the mean of five independent experiments (an average of six readings was considered for each sample). Standard deviations are represented by vertical bars. The dotted line is the trend of the experimental points (rhombus); the solid line is the best fitting straight line. * Significantly different from 0 time, p < 0.01; ** significantly different from 0 time, p < 0.001.