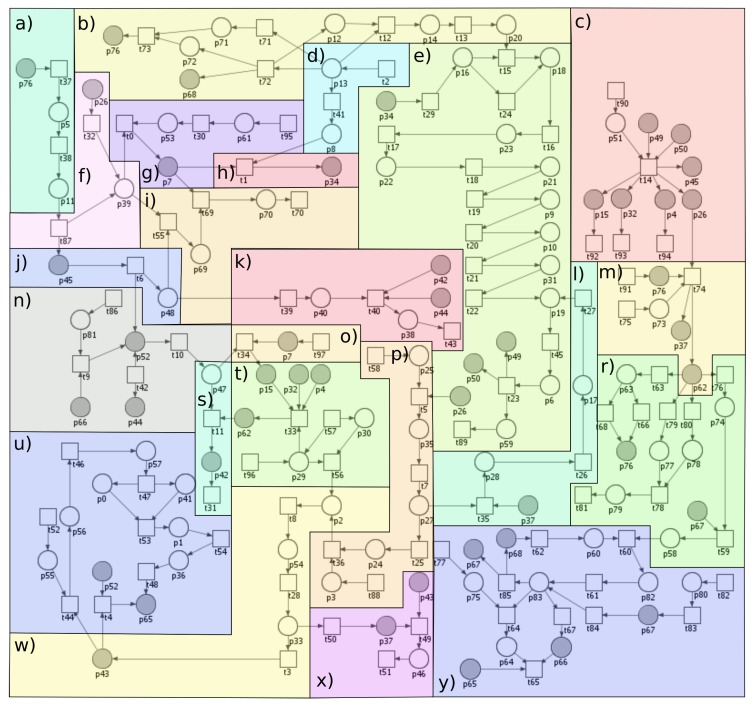
Figure 5.
The proposed model has been divided into parts corresponding to the biological phenomena: (a) Janus kinases and signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK-STAT) pathway stimulated by interferon gamma (IFN); (b) innate immune responses; (c) p50/p65 translocation to the nucleus in macrophages M1, smooth muscle cell (SMC) and endothelial cell (EC); (d) gram-negative bacterial infections; (e) activation of nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-B)—the canonical pathway via IB phosphorylation by kinase complex (IKK) (MyD88-dependent signaling pathway); (f) activation of caspase 1 (by tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and also by binding with STAT binding element (SBE) sequences of interferon regulatory factor I (IRF1); (g) IL-18 synthesis (caspase 1-dependent pathway); (h) IL-18-IL-18R complex formation; (i) negative regulation of IL-18 (by inhibition of caspase 1) caused by nitric oxide (NO); (j) NO synthesis; (k) cardiovascular disease influenced by NO-dependent pathway; (l) TNF receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2) and receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein (kinase 1 (RIP1) ubiquitination; (m) macrophages polarization; (n) lipid peroxidation (oxLDL); (o) IL-18 synthesis (caspase 1-independent pathway) and neighboring endothelial cells stimulation; (p) regulation of TNFR1 signaling; (r) the role of IL-1, IL-23, IL-6, high level of IL-10 and IL-12 (released by classically activated macrophages M1); (s) atherosclerosis progression; (t) attracting of monocytes (classically activated macrophages M1); (u) formation of apoptosome and activation of effector caspases 3, 6, 7; (w) high level of active caspase 8; (x) inhibition of caspase 8 and inhibition of apoptosis (by a high level of cFLIPs); (y) STAT6 upregulation promotes M2 macrophage polarization to suppress atherosclerosis.