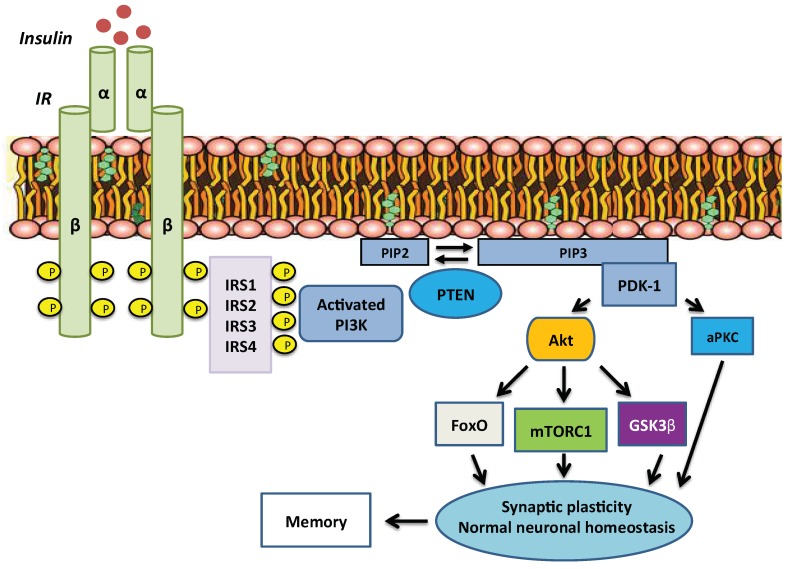
Figure 1.
Insulin signalling pathway. After insulin binding to the insulin receptor, autophosphorylation, which is essential for its activation, occurs. Then, the activated insulin receptor phosphorylates IRS proteins. IRSs activate PI3K, which catalyses the addition of a phosphate group to the membrane lipid PIP2, thereby converting it to PIP3. PTEN can convert PIP3 back to PIP2. Membrane-bound PIP3 recruits and activates PDK-1, which phosphorylates and activates Akt and atypical PKCs. Akt mediates most of insulin’s metabolic effects and in brain synaptic plasticity, neuronal homeostasis and memory. Abbreviations: IRS (insulin receptor substrate), PI3K (phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase), PIP2 (phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate), PIP3 (phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate), PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog), PDK-1 (phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1), PKC (protein kinase c), Akt (protein kinase b), mTORC1 (mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1), GSK3β (glycogen synthase kinase 3β), FoxO (forkhead box O).