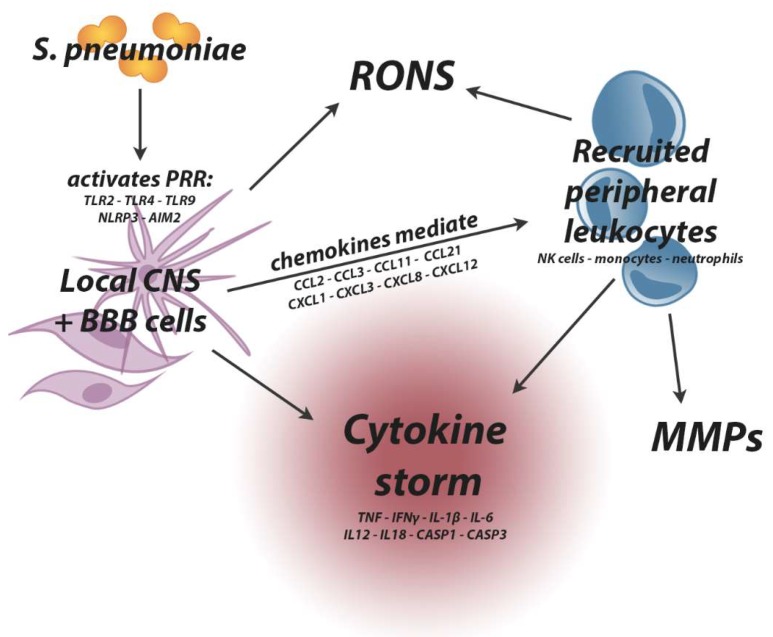
Figure 3.
Interactions between S. pneumoniae, the brain and the peripheral immune system drives pathogenesis in PM. S. pneumoniae activates resident CNS and BBB cells through PRR to initiate the inflammatory response. Chemokines released in the brain mediate recruitment and infiltration of peripheral leukocytes, including neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages and Natural Killer cells, into the brain. Local glial and endothelial cells and recruited immune cells produce RONS and cytokines, while leukocytes also produce MMPs. Black arrows indicate direction of interaction. BBB—blood‒brain barrier, CNS—central nervous system, MMPs—matrix metalloproteinases, PRR—pattern recognition receptors, RONS—reactive oxygen and nitrogen species.