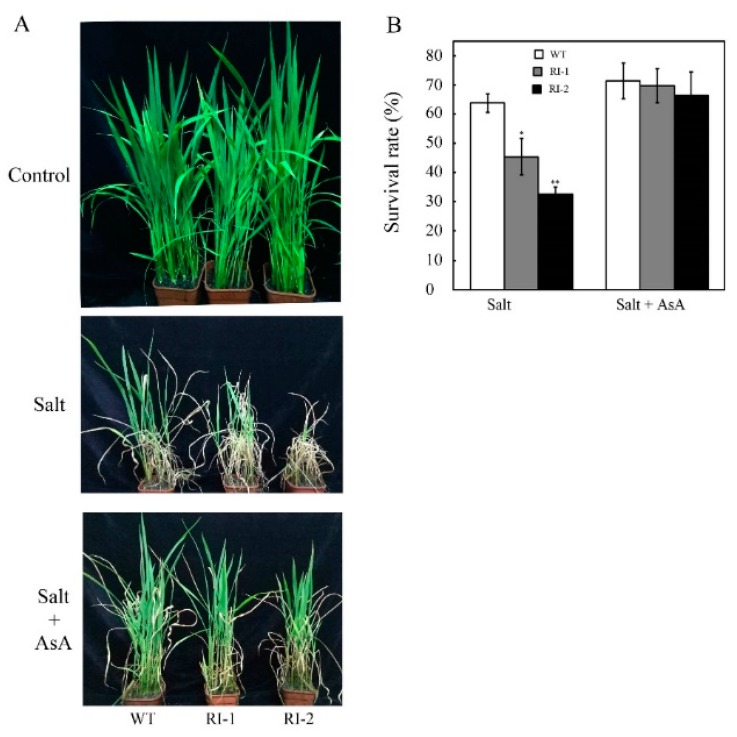
Figure 4.
Exogenous ascorbic acid (AsA) rescues the tolerance of OsVTC1-3 RI plants to salt stress. (A) Phenotype of OsVTC1-3 RI plants grown in soil with or without supplying exogenous AsA under salt treatment. (B) The survival rate of OsVTC1-1 RI plants with or without supplying exogenous AsA under salt treatment. Control indicates that rice seedlings were grown under normal conditions; NaCl indicates that rice seedlings were grown in soil by watering with 150 mM NaCl; AsA indicates that rice seedlings were grown in soil by supplied with 10 μM AsA; and NaCl + AsA represents rice seedlings grown in soil with 150 mM NaCl and 10 μM AsA. The above assays were repeated three times. About 50–60 seedlings were used in each experiment. The bars represent SE (±). The asterisk indicates results significantly different from WT (** p < 0.01 and * p < 0.05). Significance was evaluated by the t-test.