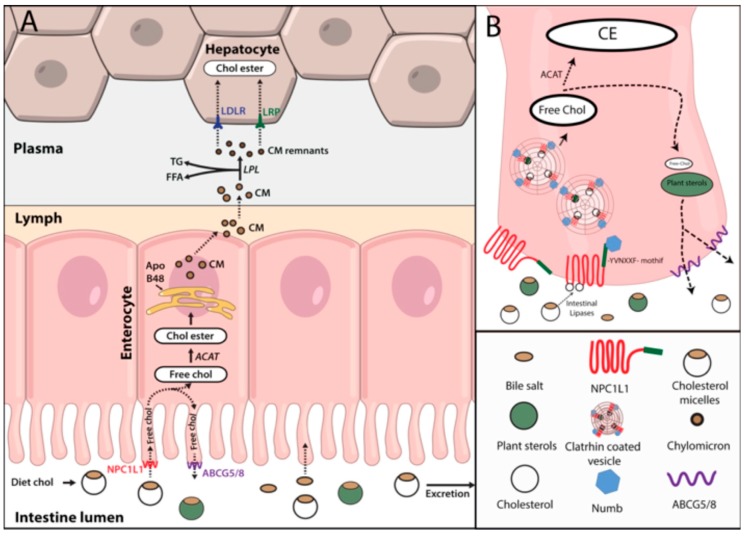
Figure 1.
Dietary cholesterol absorption. (A) Diet cholesterol forms micelles in complex with bile acids and travel across the intestinal lumen where it is hydrolyzed and taken up by Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 in the enterocyte membrane. Internalized cholesterol can either be transported back to the intestinal lumen through ABCG5/8 along with plant sterols or esterified by Acyl-CoA acyl-transferase. Esterified cholesterol within other lipids is incorporated into chylomicrons and secreted to the lymph. Once in the lymph they are drained to the plasma where by lipoprotein lipases activity lose their triglycerides and become in chylomicron remnants that are finally taken up by the liver by low density lipoprotein receptor or LDLR related proteins. (B) Free cholesterol binds NPC1L1 and promotes its conformational change. This conformational change allows the binding of Numb adapter protein to YVNXXF motif and promotes its internalization in clathrin coated pits. Abbreviations: NPC1L1: Niemann-Pick C1-like 1; ACAT: Acyl-CoA acyl-transferase; Chol ester: Esterified cholesterol; CM: Chylomicrons; LPL: lipoprotein lipases; TG: Triglycerides; FFA: Free fatty acids; LDLR: low density lipoprotein receptor; LRPs: LDLR related proteins.