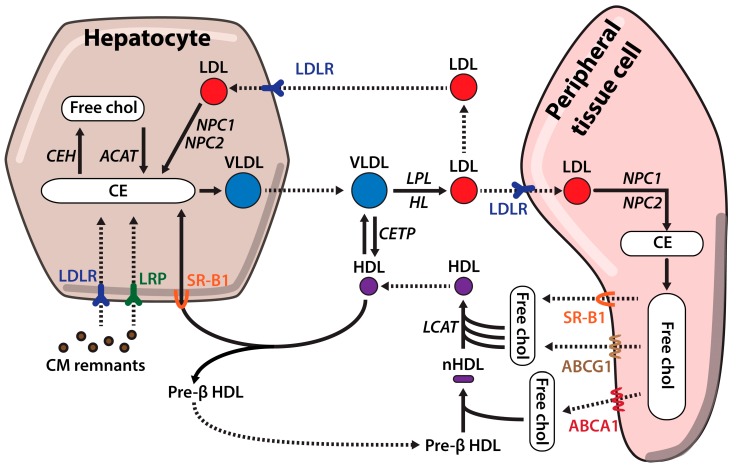
Figure 2.
Cholesterol metabolism. Cholesterol is secreted from the liver to peripheral tissues in triglyceride rich lipoproteins, very low density lipoproteins. Once in the bloodstream, VLDL are transformed into cholesterol rich LDL particles by interaction with different proteins as LPL or exchange of lipids and apolipoproteins with high density lipoproteins LDL particles are taken up by peripheral tissue cells through LDLR. Excess cholesterol from peripheral tissues is packaged in HDL lipoproteins for it clearance. First, free cholesterol is transferred to lipid poor pre-β HDL through ABCA1. Second, this first cholesterol loading changes HDL conformation and allow its interaction with ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member 1 and SR-B1 transporters that along with Lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase produce mature HDL particles that are transported back to the liver for their clearance. Abbreviations: NPC1: Niemann-Pick C1; NPC2: Niemann-Pick C2; ACAT: Acyl-CoA acyl-transferase; CM: Chylomicrons; LPL: lipoprotein lipases; TG: Triglycerides; LDLR: low density lipoprotein receptor; LRPs: LDLR related proteins; VLDL: very low density lipoproteins; HDL: high density lipoproteins; ABCG1: ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member 1; LCAT: Lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase; HDL: High density lipoproteins.