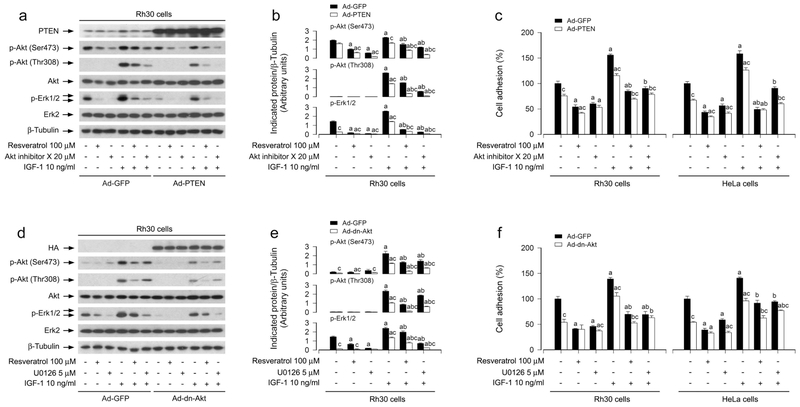
FIGURE 6.
Effects of ectopic expression of wild-type PTEN or dominant negative Akt in Rh30 and HeLa cells on resveratrol’s suppression of IGF-1-stimulated Akt/Erk1/2 activation and cell adhesion. Serum-starved Rh30 and/or HeLa cells, infected with Ad-GFP (as control), Ad-PTEN or Ad-dn-Akt, respectively, and pretreated with/without Akt inhibitor X (20 μM) or U0126 (5 μM) for 1 h, were treated with/without resveratrol (100 μM) for 4 h, followed by stimulation with/without IGF-1 (10 ng/ml) for 1 h. (a, d) Total cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting using indicated antibodies. The blots were probed for β-tubulin as a loading control. Similar results were observed in at least three independent experiments. (b, e) The blots for p-Akt (Ser473), p-Akt (Thr308), and p-Erk1/2 were semi-quantified using NIH image J. (c, f) Adherent cells were determined using CN IV-coated cell adhesion assay. Results are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3–6). a p < 0.05, difference with control group; b p < 0.05, difference with IGF-1 group; c p < 0.05, Ad-PTEN group or Ad-dn-Akt group vs. Ad-GFP group.