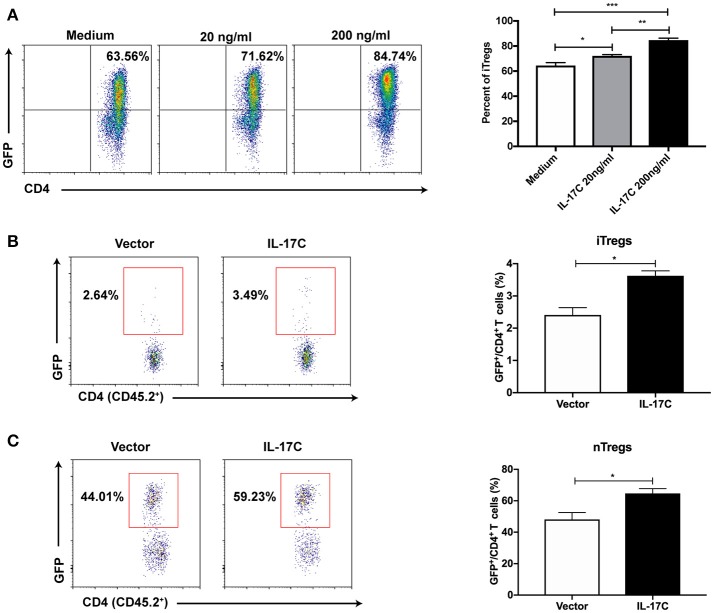
Figure 6.
IL-17C regulates both iTreg and nTreg cells during aGVHD. (A) Plate was coated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 overnight at 4°C. Naïve CD4+ T cells (CD4+CD62L+CD44−GFP−) were sorted from FoxP3-eGFP mice and seeded into 96-well plate in the presence or absence with rmIL-17C. Generation of iTreg cells were induced by rhIL-2 combined with rmTGF-β and examined 5 days later by flow cytometry. (B) BALB/C recipients were injected with IL-17C or control plasmid. 3 days later, recipients were lethally irradiated and transplanted with 1 × 10∧7 bone marrow cells from CD45.1 mice and 2 × 10∧6 naïve CD4+ T cells (CD45.2+CD4+CD62L+CD44−GFP−) from FoxP3-eGFP mice. Generation of iTregs were determined in H2-Kb+CD45.2+CD45.1−CD4+ populations at 10 days post transplantation in spleen; n = 5 per group. (C) BALB/C recipients were hydrodynamically injected with IL-17C plasmid or vector control. 3 days later, recipients were lethally irradiated and transplanted with 1 × 10∧7 bone marrow cells together with 3 × 10∧6 splenocytes from CD45.1 mice and 5 × 10∧5 nTreg cells (CD45.2+CD4+GFP+) from FoxP3-eGFP mice. GFP expression was determined in H2-Kb+CD45.2+CD45.1−CD4+ populations at 10 days post transplantation in spleen; n = 3 per group. Data are representative of two experiments and presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.