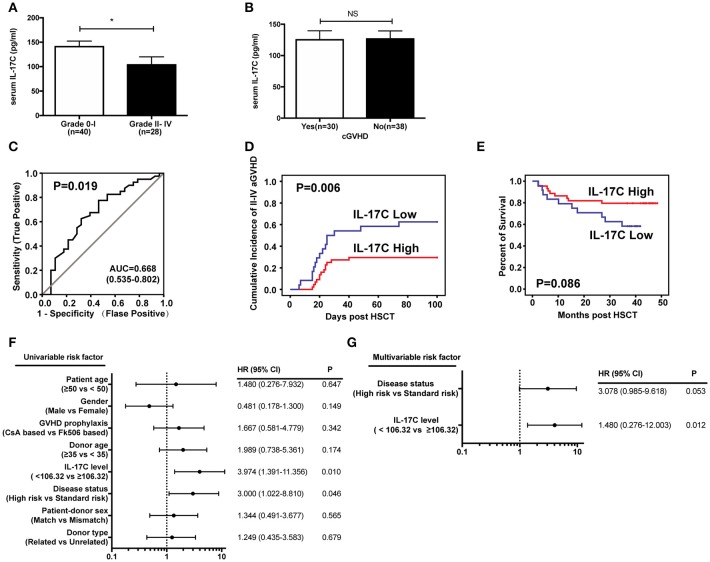
Figure 7.
IL-17C expression level predicts aGVHD incidence and severity in allo-HSCT patients. Expressions of IL-17C in human allo-HSCT patients during pre-conditioning were measured by ELISA. (A) IL-17C expression in aGVHD patients. (B) IL-17C expression in cGVHD patients. (C) Sensitivity and specificity of the analysis. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) was 0.668. The cutoff value used from the ROC curve was 106.32 pg/ml. Sensitivity and specificity was 77.5 and 53.6%, respectively. (D) The cumulative incidence of grade II-IV aGVHD was significantly lower in patients with high IL-17C expression levels by using Gray's test. (E) IL-17C-high patients showed prolonged survival compared to those with low IL-17C expression with Kaplan-Meier survival by log-rank test. (F) Univariate analyses revealed that IL-17C levels < 106.32 pg/ml were significantly associated with grade II-IV aGVHD. (G) Fine and Gray proportional hazards model analysis confirmed that low IL-17C level was the strongest parameter associated with II-IV aGVHD. *P < 0.05.