Figure 4.
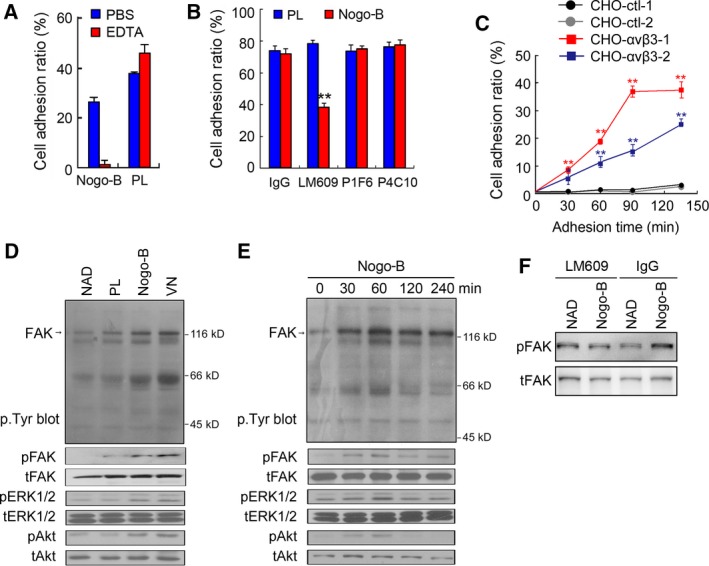
Recombinant Nogo‐B promotes cell adhesion through interacting with integrin αvβ3. (A) Effects of EDTA on HUVEC adhesion. Cells were incubated with EDTA or PBS before they were replated on Nogo‐B‐coated surfaces. (B) The cell adhesion blockade assay to investigate the effects of integrin‐neutralizing antibodies on Nogo‐B‐induced HUVEC adhesion. Cells were incubated with neutralizing anti‐integrin antibodies as indicated before they were replated on Nogo‐B‐coated surfaces. LM609, anti‐integrin αvβ3 antibody; P1F6, anti‐integrin αvβ5 antibody; and P4C10, anti‐integrin β1 antibody. Polylysine was used as an integrin‐independent control. The error bar represents the SD (n = 3, **P < 0.01). (C) Effect of Nogo‐B expression on CHO cell adhesion. Two CHO control cell lines (CHO‐ctl‐1, CHO‐ctl‐2) and two CHO stable cell lines expressing integrin αvβ3 (CHO‐αvβ3‐1, CHO‐αvβ3‐2) were replated on the Nogo‐B‐coated surface, and cell adherence was determined at different time points. The error bar represents the SD (n = 3, **P < 0.01). (D) FAK phosphorylation assay. The levels of indicated phosphorylated and total protein were detected in whole cell lysate (WCL) from cells adhered to PL, Nogo‐B, or vitronectin (VN)‐coated surfaces or cells in suspension (NAD). (E) Time course studies of different protein phosphorylation for cells grown on Nogo‐B‐coated surfaces. (F) FAK phosphorylation analysis after HUVEC was blocked by integrin αvβ3 neutralizing antibody.
