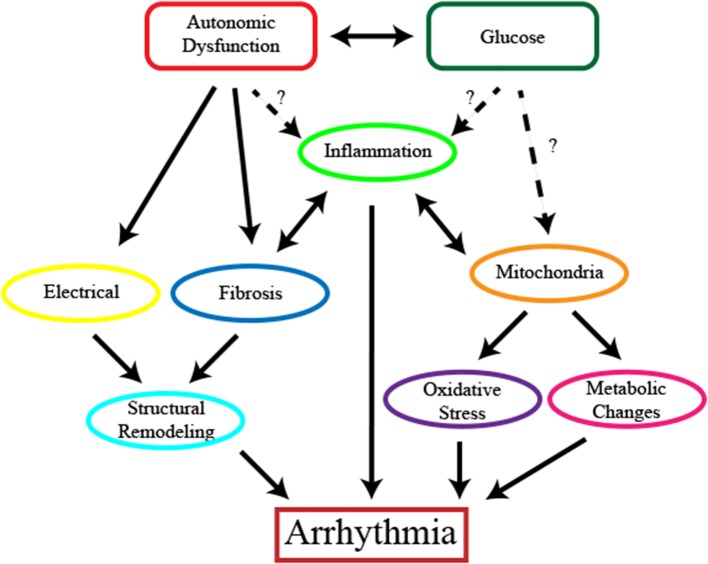
Figure 1.
The complex relationship between diabetes and cardiac arrhythmias. Potential contributors to the induction of cardiac arrhythmias including hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia or glucose fluctuations and autonomic dysfunction activate multiple mechanisms to contribute to the development of cardiac arrhythmias. Structural remodeling including changes in the electrical conduction of the heart and fibrosis promote and potentiate the progression of the disease. Mitochondrial dysfunction leads to changes in cardiomyocyte function and metabolism and contributes to disease progression through oxidative stress. Inflammation is present and may arise as a result of oxidative stress and structural changes.