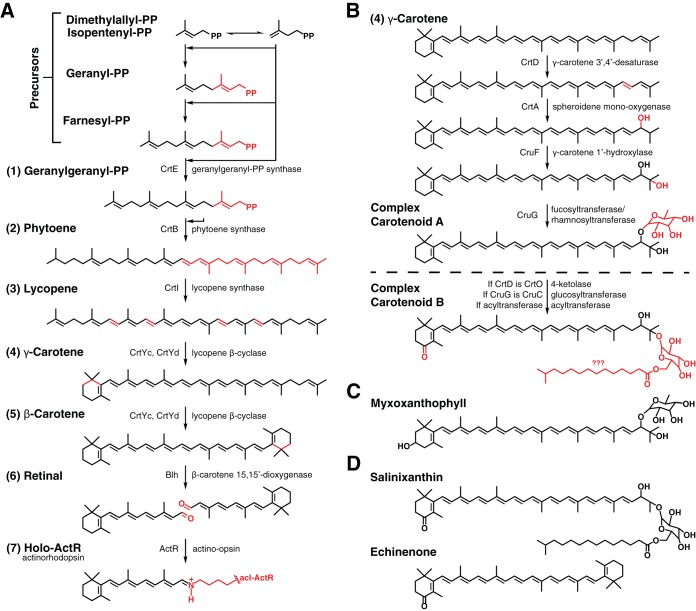
FIG 3.
Predicted carotenoid-related pathways in acI. (A) The actinorhodopsin synthesis pathway requires isopentenyl precursors to be assembled into carotenoids (1 to 3), which are modified (4 to 5) and cleaved to produce retinal (6). A Schiff base forms between retinal and a lysine of acI-ActR to form acI-holo-ActR (7). Chemical changes are shown in red, proteins from this study with their predicted functions are shown to the sides of progress arrows, and product names are shown to left of their chemical structures. Step 6 cannot be performed in acI Actinobacteria that lack Blh; retinal must be exogenously sourced. (B) A complex carotenoid synthesis pathway is predicted to require γ-carotene produced in the actinorhodopsin pathway, with further desaturation, hydroxylation, and glycosylation for a myxoxanthophyll-like carotenoid. A carotenoid with different stucture can result if enzyme identities are different and a proposed acyltransferase is involved in the pathway. Question marks indicate uncertainty in naming and/or chemical structure. (C) A complex carotenoid used by many cyanobacteria for photosynthesis. (D) Complex carotenoids from other organisms that function as carotenoid antennae on proton-pumping rhodopsins.