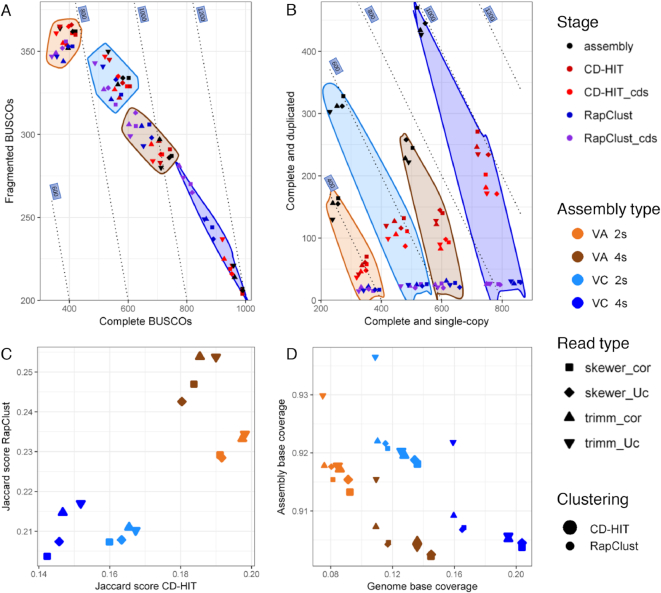
Figure 5:
Evaluation of assembly and clustering methods for Trinity transcriptomes. Completeness assessment with BUSCO tool subdivided into complete vs fragmented BUSCOs (A) or single-copy vs duplicated complete BUSCOs (B). Dotted lines represent isolines of BUSCO numbers from a total search space of 1,440 orthologs. Dot colors indicate assembly stage and areas assembly type. Stages of the assembly are divided into initial de novo assembly (asmb), clustered with either CD-HIT or RapClust, or predicted coding regions (cds). Assembly type indicates the combination of blueberry species (V.arboreum, VA; V. corymbosum, VC) and the use of two independent assemblies merged (2s) or assembly of four samples (4s). Shapes represent read pre-processing options, with (cor) or without (Uc) error correction, and the use of Skewer or Trimmomatic (trimm) trimming tools. (C) Distribution of mean Jaccard scores on CD-HIT and RapClust clusters of transcriptome assemblies. Scores range between ∼0 (low clustering of co-annotated transcripts) and 1 (perfect clustering of co-annotated transcripts). (D) Distribution of genome vs assembly base coverage on multiple de novo assemblies mapped to V. corymbosum reference genome after redundancy reduction with either CD-HIT (larger points) or RapClust (smaller points). Shapes indicate read processing, with (cor) or without (Uc) error correction, and trimmed with either Trimmomatic (trimm) or Skewer.