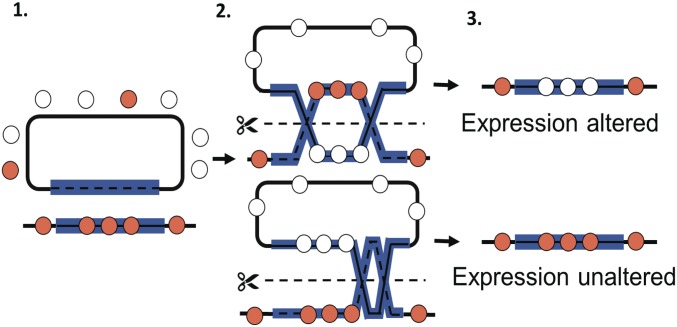
Fig. 2.
Model for displacement of native SARC chromatin proteins by recombination. (1, Left) SARC strains contains a mixture of SARC (orange) and non-SARC (white) chromatin proteins. Chromosomal SARC genes are bound by native SARC chromatin proteins that confer its expression state. Homologous plasmid DNA is naked. (2, Center) During recombination, rad54-mediated branch migration displaces chromatin proteins while replacing native chromatin segments with naïve DNA. In the absence of acid selection, chromatin proteins can repopulate these regions in non-SARC patterns. Depending on the crossover location, different lengths of chromatin can be exchanged. (3, Right) Resulting gene regions have no sequence changes, but are bound fully or partially by reassociated non-SARC chromatin patterns.