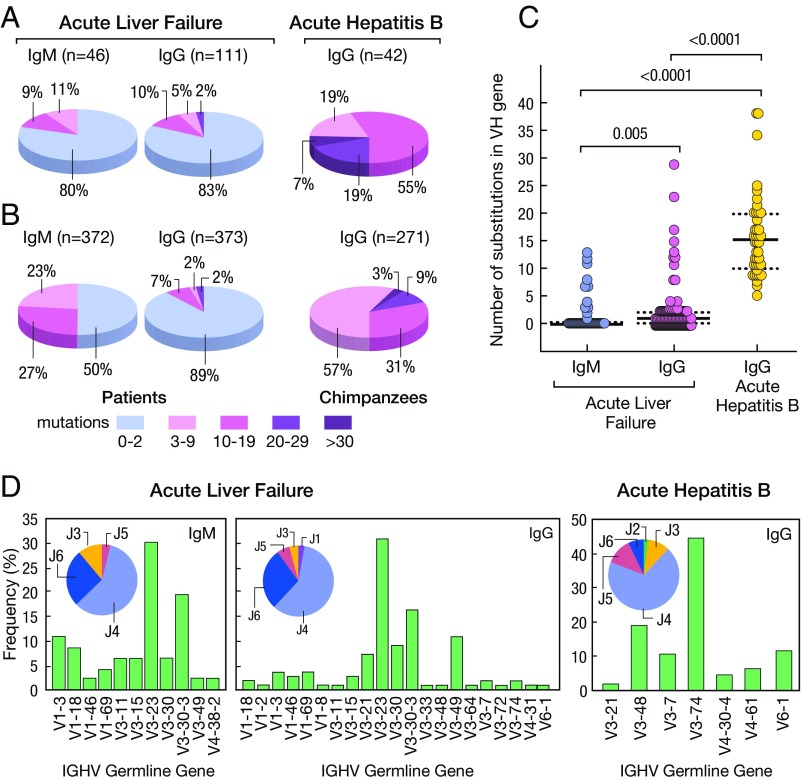
Fig. 6.
Characteristics of HBcAg-specific antibodies isolated from liver tissues of four patients with HBV-associated ALF and two chimpanzees with classic self-limited acute hepatitis B. (A) Proportion of variable genes from IgM (n = 46) and IgG (n = 111) detected in the livers of four patients with ALF or IgG (n = 46) from two chimpanzees with acute hepatitis B. The number of somatic mutations is identified by a different color. The percentage of antibodies in germline configuration as well as of those with different degrees of somatic hypermutation mutations are shown both in ALF and in classic acute hepatitis B in chimpanzees. (B) Abundance of antibodies with different degrees of mutations following three cycles of panning of the IgG and IgM libraries on HBcAg. (C) Average frequency of somatic mutations among IgM and IgG sequences of ALF patients or IgG from the two chimpanzees. Solid lines show the medians; dotted lines represent the interquartile range. P values refer to comparisons performed using the two-tailed Mann–Whitney test. (D) Frequency of IGHV and HJ genes used by HBcAg-specific IgM and IgG obtained from patients with ALF and IgG from chimpanzees with acute hepatitis B.