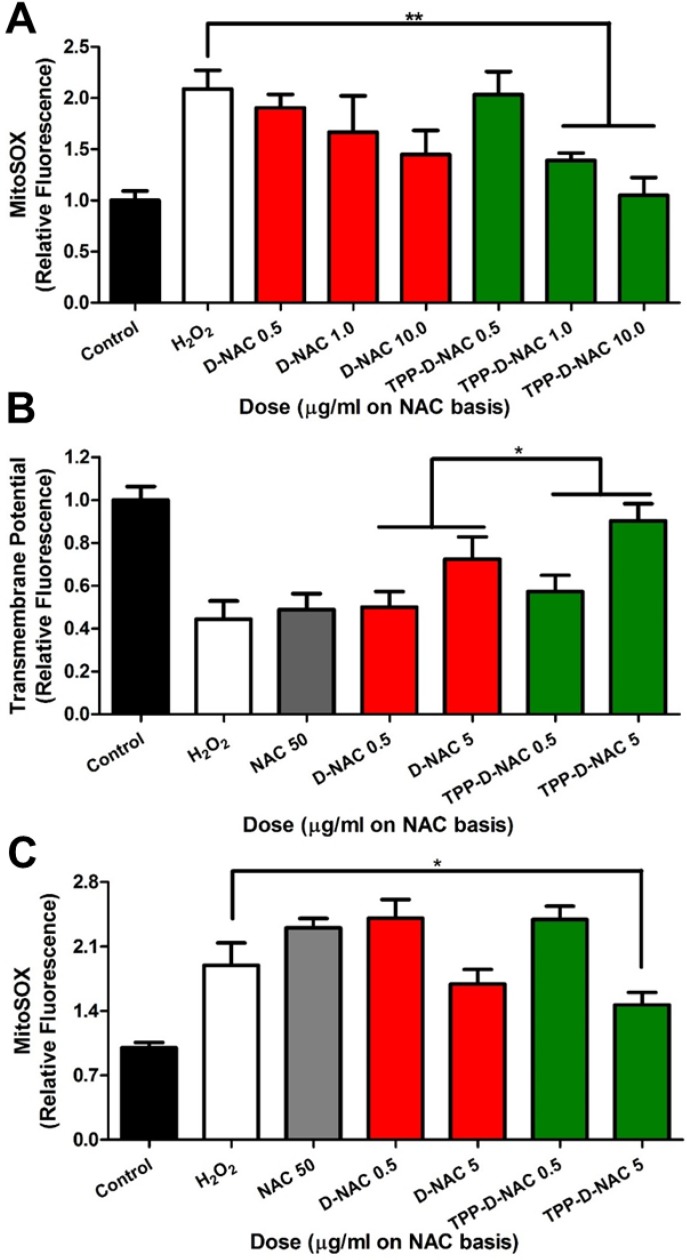
Figure 5.
TPP conjugation enhances therapeutic efficacy of D-NAC in mitochondrial oxidative stress. A For acute oxidative stress injury, BV2 murine microglia were stimulated with 50 µM H2O2 for 2 hours, then treated with dendrimer for 6 hours, and analyzed with MitoSOX to measure mitochondrial superoxide levels. When compared to the H2O2 group, TPP-D-NAC exhibits a significant dose-dependent reduction in mitochondria superoxide while D-NAC did not under conditions of oxidative stress. ** p < 0.01 in Student's t-test compared to H2O2 group. B TPP-D-NAC ameliorates oxidative stress-induced membrane depolarization. * p < 0.05, F = 5.632 with treatment in two-way ANOVA. C For long term oxidative stress insult, cells were stimulated with 50 µM H2O2 for 2 hours, followed by cotreatment of free NAC, D-NAC, or TPP-D-NAC with 5 µM H2O2 for 24 hours. TPP-D-NAC exhibits greater reduction in mitochondrial superoxide than DNAC and free NAC. * p < 0.05 in Student's t-test compared to H2O2 group.